Severe Leukoplakia of the Vagina and Cervix Successfully Treated with Intravaginal Application of Topical Glucocorticoids
Article Information
M Condic1*, A Mustea1, DJ Ralser1, J Wenzel2, C Braegelmann2
1Department of Gynecology and Gynecological Oncology, University Hospital Bonn, Germany
2Clinic for Dermatology and Allergy, University Hospital Bonn, Germany
*Corresponding Author: Mateja Condic, Department of Gynecology and Gynecological Oncology, University Hospital Bonn, Germany
Received: 18 January 2022; Accepted: 27 January 2022; Published: 10 February 2022
Citation: M Condic, A Mustea, DJ Ralser, J Wenzel, C Braegelmann. Severe Leukoplakia of the Vagina and Cervix Successfully Treated with Intravaginal Application of Topical Glucocorticoids. Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports 6 (2022): 63-65.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
Leukoplakia of the vagina and cervix can hide (pre)malignant lesions or be caused by them, so biopsy and treatment is mandatory. Here we present a rare case of severe leukoplakia of the vagina and the cervix due to a chronic inflammatory reaction, which was successfully treated with intravaginal application of budesonide foam. In vulvar lesions, topical glucocorticoids are first line treatment, whereas intravaginal application is rare and pharmaceutical market lacks products for this indication. We describe a unique, well tolerated and successful treatment of chronic inflammatory reactions of the vagina and cervix resulting in quick and complete remission.
Keywords
Chronic inflammation; Cervical neoplasma; Hyperkeratosis; Leukoplakia
Chronic inflammation articles; Cervical neoplasma articles; Hyperkeratosis articles; Leukoplakia articles
Chronic inflammation articles Chronic inflammation Research articles Chronic inflammation review articles Chronic inflammation PubMed articles Chronic inflammation PubMed Central articles Chronic inflammation 2023 articles Chronic inflammation 2024 articles Chronic inflammation Scopus articles Chronic inflammation impact factor journals Chronic inflammation Scopus journals Chronic inflammation PubMed journals Chronic inflammation medical journals Chronic inflammation free journals Chronic inflammation best journals Chronic inflammation top journals Chronic inflammation free medical journals Chronic inflammation famous journals Chronic inflammation Google Scholar indexed journals COVID-19 articles COVID-19 Research articles COVID-19 review articles COVID-19 PubMed articles COVID-19 PubMed Central articles COVID-19 2023 articles COVID-19 2024 articles COVID-19 Scopus articles COVID-19 impact factor journals COVID-19 Scopus journals COVID-19 PubMed journals COVID-19 medical journals COVID-19 free journals COVID-19 best journals COVID-19 top journals COVID-19 free medical journals COVID-19 famous journals COVID-19 Google Scholar indexed journals Cervical neoplasma articles Cervical neoplasma Research articles Cervical neoplasma review articles Cervical neoplasma PubMed articles Cervical neoplasma PubMed Central articles Cervical neoplasma 2023 articles Cervical neoplasma 2024 articles Cervical neoplasma Scopus articles Cervical neoplasma impact factor journals Cervical neoplasma Scopus journals Cervical neoplasma PubMed journals Cervical neoplasma medical journals Cervical neoplasma free journals Cervical neoplasma best journals Cervical neoplasma top journals Cervical neoplasma free medical journals Cervical neoplasma famous journals Cervical neoplasma Google Scholar indexed journals Hyperkeratosis articles Hyperkeratosis Research articles Hyperkeratosis review articles Hyperkeratosis PubMed articles Hyperkeratosis PubMed Central articles Hyperkeratosis 2023 articles Hyperkeratosis 2024 articles Hyperkeratosis Scopus articles Hyperkeratosis impact factor journals Hyperkeratosis Scopus journals Hyperkeratosis PubMed journals Hyperkeratosis medical journals Hyperkeratosis free journals Hyperkeratosis best journals Hyperkeratosis top journals Hyperkeratosis free medical journals Hyperkeratosis famous journals Hyperkeratosis Google Scholar indexed journals Ultra Sound articles Ultra Sound Research articles Ultra Sound review articles Ultra Sound PubMed articles Ultra Sound PubMed Central articles Ultra Sound 2023 articles Ultra Sound 2024 articles Ultra Sound Scopus articles Ultra Sound impact factor journals Ultra Sound Scopus journals Ultra Sound PubMed journals Ultra Sound medical journals Ultra Sound free journals Ultra Sound best journals Ultra Sound top journals Ultra Sound free medical journals Ultra Sound famous journals Ultra Sound Google Scholar indexed journals treatment articles treatment Research articles treatment review articles treatment PubMed articles treatment PubMed Central articles treatment 2023 articles treatment 2024 articles treatment Scopus articles treatment impact factor journals treatment Scopus journals treatment PubMed journals treatment medical journals treatment free journals treatment best journals treatment top journals treatment free medical journals treatment famous journals treatment Google Scholar indexed journals CT articles CT Research articles CT review articles CT PubMed articles CT PubMed Central articles CT 2023 articles CT 2024 articles CT Scopus articles CT impact factor journals CT Scopus journals CT PubMed journals CT medical journals CT free journals CT best journals CT top journals CT free medical journals CT famous journals CT Google Scholar indexed journals Lymphangioma articles Lymphangioma Research articles Lymphangioma review articles Lymphangioma PubMed articles Lymphangioma PubMed Central articles Lymphangioma 2023 articles Lymphangioma 2024 articles Lymphangioma Scopus articles Lymphangioma impact factor journals Lymphangioma Scopus journals Lymphangioma PubMed journals Lymphangioma medical journals Lymphangioma free journals Lymphangioma best journals Lymphangioma top journals Lymphangioma free medical journals Lymphangioma famous journals Lymphangioma Google Scholar indexed journals surgery articles surgery Research articles surgery review articles surgery PubMed articles surgery PubMed Central articles surgery 2023 articles surgery 2024 articles surgery Scopus articles surgery impact factor journals surgery Scopus journals surgery PubMed journals surgery medical journals surgery free journals surgery best journals surgery top journals surgery free medical journals surgery famous journals surgery Google Scholar indexed journals Leukoplakia articles Leukoplakia Research articles Leukoplakia review articles Leukoplakia PubMed articles Leukoplakia PubMed Central articles Leukoplakia 2023 articles Leukoplakia 2024 articles Leukoplakia Scopus articles Leukoplakia impact factor journals Leukoplakia Scopus journals Leukoplakia PubMed journals Leukoplakia medical journals Leukoplakia free journals Leukoplakia best journals Leukoplakia top journals Leukoplakia free medical journals Leukoplakia famous journals Leukoplakia Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
1. Synopsis of the Case
A 20-year old patient was referred to our gynecological department for colposcopy due to severe leukoplakia of the upper part of the vagina and cervix having persisted for more than one year. Two years before, she had been diagnosed with low grade intraepithelial lesion of the cervix. Now, PAP smear cytology and HPV diagnostic were normal. She had received HPV vaccination as a teenager. She was an occasional smoker and did not suffer from chronic/autoimmune/dermatological diseases or allergies. For several years, she was taking a combined oral contraceptive pill. Several vaginal suppositories (antibiotics, lactobacillus, clotrimazol) had failed to achieve healing up. The colposcopy of the vagina and the cervix showed an extensive hyperkeratosis of the upper part of the vagina and the cervix (see Figure 1a). Due to tissue rigidity superficial loop electrical excision and laser therapy were necessary to obtain a sample after standard procedure for biopsy taking had failed. Complete surgical treatment was impossible due to size of the leukoplakia. Histological examination revealed compact hyperkeratosis partially as parakeratosis above acanthotic epidermis featuring a pronounced stratum granulosum and mild spongiosis as well as perinuclear vacuolization of keratinocytes. Sparse inflammatory infiltrate with exocytosis of single lymphocytes was detected. No signs of malignancy were present. Findings were considered conformable with chronic inflammation or viral acanthoma. Immunohistochemistry and molecular pathology for HPV were negative (see Figure 2).
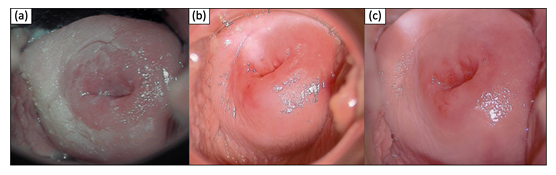
Figure 1: Timeline of clinical findings (colposcopy pictures). (a) initial finding (b) + 2 weeks treatment (c) + 3 months maintenance therapy
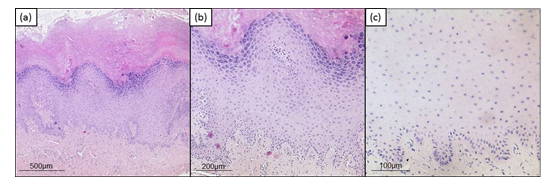
Figure 2: Histologic findings. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining, original magnification x50. (b) Hematoxylin and eosin staining, original magnification x100. (c) HPV staining (Anti Human Papilloma virus (HPV) Clone K1H8, Dako / Agilent (M3528), 1:50, pretreatment pH 6,0) original magnification x200.
In summary, as there were no signs for (pre)malignant lesions, HPV infection or any other acute disease, we decided to perform a local treatment with corticosteroids as the leading signs of histological analysis showed chronic inflammation. Besides discontinuation of oral contraceptives the patient hence applied budesonid rectal foam intravaginally once daily for 15 days. Subsequent colposcopy after two weeks showed complete remission (see Figure 1b). The patient did not have any discomfort. Budesonid foam was continued every three days for three months. Colposcopy did not show a relapse of the leukoplakia (see Figure 1c). Consequently, Budesonid application was discontinued which did not result in any relapse.
2. Discussion
Leukoplakia of the cervix appears as a white plaque before application of acetic acid. White coloration is caused by excessive keratin deposition and relative vascularity in epithelial cells. Leukoplakia can be idiopathic or induced by HPV infection. Also, cervical neoplasms and high grade lesions can induce keratin deposit and appear as leukoplakia. As they can hide premalignant lesions, leukoplakia patches in the transformation zone of the cervix should be biopsied [1]. In our case, we did not find a causal reason for the chronic inflammatory reaction underlying the severe leukoplakia. Sometimes, contraceptives can impact the vaginal microflora and genital tract immune cells enhancing the risk for infections [2]. Leukoplakia of the oral cavity is the most common potentially malignant lesion and there appears to be some link between HPV infection and carcinomatous transformation [3]. Vulvar leukoplakia is most often associated with lichen sclerosis and is treated with topical corticosteroids due to risk of malignancy [4]. As cervical leukoplakia can hide (pre)malignant lesions or be caused by them, biopsy and treatment is essential. Compared to vulvar lesions, where topical glucocorticoids are first line treatment, intravaginal application is rare and pharmaceutical market lacks products for this indication.
3. Conclusion
Our case showed a unique, successful and well tolerated treatment with intravaginal application of budesonid foams, resulting in a quick and complete remission of an extensive leukoplakia of the vagina and cervix.
References
- Küppers VR. Revidierte kolposkopische und zytologische Nomenklaturen. Gynäkologe (2016).
- Achilles SL, Hillier SL. The complexity of contraceptives: understanding their impact on genital immune cells and vaginal microbiota. AIDS 27 (2013): S5-15.
- Feller L, Lemmer J. Cell transformation and the evolution of a field of precancerization as it relates to oral leukoplakia. Int J Dent 2011 (2011): 321750.
- Yordanov A, Tantchev L, Kostov S, et al. Vulvar leukoplakia: therapeutic options. Prz Menopauzalny 19 (2020): 135-139.
