Multi-Dimensional Implication of Water Scarcity on Inhibitants of District Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan
Article Information
Sadia Barrech1, Syed Ainuddin2, Najeebullah3*
1Department of Social Work, University of Balochistan, Quetta, Pakistan
2Department of Disaster Management and Development Studies, University of Balochistan, Quetta, Pakistan
3Department of Geology, University of Balochistan, Quetta, Pakistan
*Corresponding Author: Najeebullah, Department of Geology, University of Balochistan, Quetta, Pakistan
Received: 11 May 2018; Accepted: 12 July 2018; Published: 04 October 2018
Citation: Sadia Barrech, Syed Ainuddin, Najeebullah. Multi-Dimensional Implication of Water Scarcity on Inhibitants of District Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan. Journal of Environmental Science and Public Health 2 (2018): 136-143.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
Water is the fundamental need of living being. It is necessary for manageable advancement, including the protection of common habitat, mitigation of destitution and craving. Like other nations a number of areas in Pakistan are also facing the problem of water scarcity. The present investigation has been made to explore various implications of water scarcity on inhibitants of Quetta district Balochistan. The study depends on essential information gathered from agriculturists and different personals through focused group discussions and questionnaire survey. Stratified random sampling was the method of sampling whereas the sample size was 400. For statistical significance chi square was used keeping level of significance as 0.05. Although no association could be established among the study groups, however, the results clearly indicate that the level of ground and surface water is scarce. The scarcity of Water has negatively impacted the agriculture, trees, economy and health of the people of the study area. The scarcity of water has also compelled people for migration to other areas. The results of study suggests that government should make further dams, guiding the population and the framers on proper use of water and advocating the general public to obey regulations regarding water mining.
Keywords
Water scarcity, Inhibitants, Chi square test, Water mining
Water scarcity articles Water scarcity Research articles Water scarcity review articles Water scarcity PubMed articles Water scarcity PubMed Central articles Water scarcity 2023 articles Water scarcity 2024 articles Water scarcity Scopus articles Water scarcity impact factor journals Water scarcity Scopus journals Water scarcity PubMed journals Water scarcity medical journals Water scarcity free journals Water scarcity best journals Water scarcity top journals Water scarcity free medical journals Water scarcity famous journals Water scarcity Google Scholar indexed journals Inhibitants articles Inhibitants Research articles Inhibitants review articles Inhibitants PubMed articles Inhibitants PubMed Central articles Inhibitants 2023 articles Inhibitants 2024 articles Inhibitants Scopus articles Inhibitants impact factor journals Inhibitants Scopus journals Inhibitants PubMed journals Inhibitants medical journals Inhibitants free journals Inhibitants best journals Inhibitants top journals Inhibitants free medical journals Inhibitants famous journals Inhibitants Google Scholar indexed journals Chi square test articles Chi square test Research articles Chi square test review articles Chi square test PubMed articles Chi square test PubMed Central articles Chi square test 2023 articles Chi square test 2024 articles Chi square test Scopus articles Chi square test impact factor journals Chi square test Scopus journals Chi square test PubMed journals Chi square test medical journals Chi square test free journals Chi square test best journals Chi square test top journals Chi square test free medical journals Chi square test famous journals Chi square test Google Scholar indexed journals Water mining articles Water mining Research articles Water mining review articles Water mining PubMed articles Water mining PubMed Central articles Water mining 2023 articles Water mining 2024 articles Water mining Scopus articles Water mining impact factor journals Water mining Scopus journals Water mining PubMed journals Water mining medical journals Water mining free journals Water mining best journals Water mining top journals Water mining free medical journals Water mining famous journals Water mining Google Scholar indexed journals water articles water Research articles water review articles water PubMed articles water PubMed Central articles water 2023 articles water 2024 articles water Scopus articles water impact factor journals water Scopus journals water PubMed journals water medical journals water free journals water best journals water top journals water free medical journals water famous journals water Google Scholar indexed journals ground and surface water articles ground and surface water Research articles ground and surface water review articles ground and surface water PubMed articles ground and surface water PubMed Central articles ground and surface water 2023 articles ground and surface water 2024 articles ground and surface water Scopus articles ground and surface water impact factor journals ground and surface water Scopus journals ground and surface water PubMed journals ground and surface water medical journals ground and surface water free journals ground and surface water best journals ground and surface water top journals ground and surface water free medical journals ground and surface water famous journals ground and surface water Google Scholar indexed journals ground water articles ground water Research articles ground water review articles ground water PubMed articles ground water PubMed Central articles ground water 2023 articles ground water 2024 articles ground water Scopus articles ground water impact factor journals ground water Scopus journals ground water PubMed journals ground water medical journals ground water free journals ground water best journals ground water top journals ground water free medical journals ground water famous journals ground water Google Scholar indexed journals tube wells articles tube wells Research articles tube wells review articles tube wells PubMed articles tube wells PubMed Central articles tube wells 2023 articles tube wells 2024 articles tube wells Scopus articles tube wells impact factor journals tube wells Scopus journals tube wells PubMed journals tube wells medical journals tube wells free journals tube wells best journals tube wells top journals tube wells free medical journals tube wells famous journals tube wells Google Scholar indexed journals water scarcity articles water scarcity Research articles water scarcity review articles water scarcity PubMed articles water scarcity PubMed Central articles water scarcity 2023 articles water scarcity 2024 articles water scarcity Scopus articles water scarcity impact factor journals water scarcity Scopus journals water scarcity PubMed journals water scarcity medical journals water scarcity free journals water scarcity best journals water scarcity top journals water scarcity free medical journals water scarcity famous journals water scarcity Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
1. Introduction
Water is one of the basic needs for life. It is in essential source driving the economy of nations hence, crucial for their wellbeing and prosperity [1]. All foods and fruiticious supplements use ingredients dependent upon water [2]. A number of nations are confronting the challenge of increasing water demand due to increase and population and economic growth. Water places a key role in areas of social interests like industrialization and urbanization [3]. The administration and management of water supplies is subjected to political, social and monitory problems [4]. Creative methodologies can be used to understand efficient water distribution [5]. The agri based economy of Pakistan is also significantly affected by water shortage. The province of Balochistan is among the most drastic affected list. Climatically Balochistan ranges from semiarid to hyperarid state portrayed by rare and spatially dispersed rainfall and high evaporation rates. The special accessibility of water in the area is 30% of Pakistan. One of the big reasons of water shortage is high stream slobs which causes the water to run quickly [6]. The economy of Balochistan is mainly depended upon farming and livestock. A number of crops, vegetables, deciduous and tropical fruits are produced by the farmers in Balochistan due to vide agro environmental conditions [7]. The agri business depends of both ground and surface water reservoirs. Flood, feeder and Khirthar canals from Indus Basin irrigation system are the means of surface water whereas, the main sources of ground water include springs, crazes, tube wells and wells. Wastage of surface water and aimless misuse of ground water has made administration of water a complex issue in Balochistan. The increased installation of tube wells with passage of time has also worsened the problem.
In a related study conducted in Pashin Lora Basin it has been reported that reservoirs of water are depleting with time which may lead to catastrophy if proper measures are not taken for preservation [6]. In another study conducted by Shah et al. [8] it has been stated that due to overexploitation and mishandling the agriculturists are facing serious water problems in Balochistan. Nasurullah et al. [9] have worked on the financial impacts on water shortage in Tahsel Karezat District Pishin Balochistan. They have reported that the yearly rate of water table consumption is accruing in the range from 10 to 60 feet for each annum.
Khair et al. [10] evaluated that groundwater levels in the upland Balochistan are declining at a disturbing rate of two to three meters every year. They recommended that a more far reaching reasonable groundwater administration strategy with the association of the considerable number of partners is required. The above writing demonstrates that water shortage is an issue in the investigation territory of Quetta District Balochistan. To further elaborate the effects of water scarcity in the study area the present investigation has been carried out.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1 Sample size
The district Quetta, which sonsists of chiltan and Zarghoon towns, was selected as study population in this investigation. As objectives of the very drudgery were to analyze the socio-economic impact of the scarcity of water in District Quetta, therefore, farming community and Urban consumers of Quetta were mainly targeted. The total population of district Quetta is about 759941 District Census Reports (1998), however, a sample size of four hundred people through stratified random sampling technique was calculated for the study using Arkin and Colton formula [11] as shown below.

Where
n=sample size, N=population size, Z=confidence level (95%=1.96), P=degree of variability (50%) and E=level of precision or sampling error which is 50%.
2.2 Sampling tool
Focused group discussion and structured questionnaire were used to collect the data. The questionnaire was validated by pretesting small sample size before using at larger level.
2.3 Statistical analysis
The collected data was coded and then double entered using software MS Excel version 2007. MS Excel (Version 2007) and Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS, version 2015) were used for descriptive (Max, Min) and inferential statistics (Chi Square Test), respectively. The significance threshold was set at 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
On the basis of the very section the consequences and discussion of the study are focused. Furthermore the very segment is distributed into 2 sub-sections. The first sub-section elaborates the opinion of local population in regards to the social impact of the scarcity of water in Quetta. The other sub part delineates the economic impact of water shortage on distinct agronomic segments of the economy.
3.1 Water scarcity causes poverty
Water being the most essential part of the wellbeing has occupied the life’s verbum part. The survival could even not be thought without it. The under discussion survey has depicted that not only the survival is impossible without water but it also has effect on the other grounds of life. In Quetta region this is one of the key causes of poverty. As shown in Figure 1, out of 400 individuals 238 (59.5% of the total sample sizes) were of opinion that water scarcity causes poverty while, the rest 162 (40.5%) having of the view that water scarcity does not cause any poverty. A chi square test of independence was used to find any association between the two groups. The p value of 0.157 was obtained which is greater than the chosen significance level (?=0.05) hence it is concluded that there is no association between the two groups at 0.05 significance level.
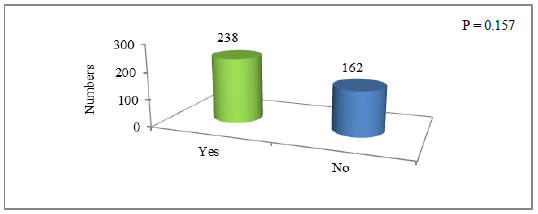
Figure 1: Survey response showing water scarcity causing poverty in Quetta Balochistan.
3.2 Poverty causes water scarcity
The response of individuals on statement that poverty is the cause of water scarcity has been reported in Figure 2. Around 281 individuals (70.25% of the total sample size) were thinking that poverty causing water scarcity in Quetta Bulichistan whereas, the rest 119 (29.75%) did not agree with the statement. The chi square p value of 0.157 was obtained which is greater than the chosen significance level (?=0.05) hence it is concluded that there is no association between the two groups at 0.05 significance level.
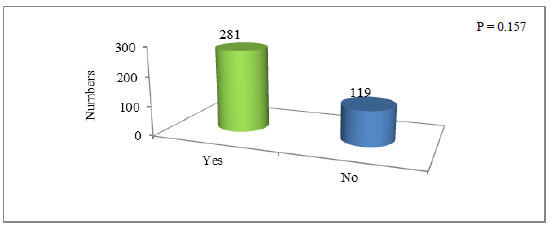
Figure 2: Survey response showing poverty causing water scarcity in Quetta Balochistan.
3.3 Water scarcity impact on agriculture
The life of agriculture relies on water. The scarcity of water is one of the big threats to agriculture. Water scarcity not only affects the life of trees but also deprives the masses from food supplements. Agriculture is one of the best sources of the economy of the people of Quetta. A study conducted by [12] has reported that owing to water scarcity a large number of distinct fruity plants have dried. In the current survey it was found that half of the sampled population was of the thought that water scarcity has direct impact on the economy of the agriculture dependent people whereas the rest half were denying its effect on the economy. The results have been shown in Figure 3. The chi square p value for this data is also 0.157 which is greater than the chosen significance level (?=0.05) hence it is concluded that there is no association between the two groups at 0.05 significance level.
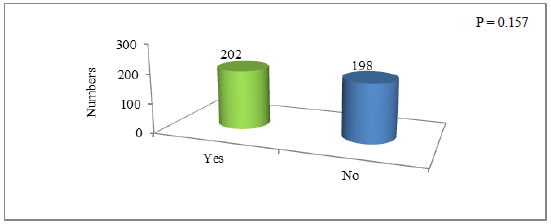
Figure 3: Survey response showing water scarcity impact on income of farmers.
3.4 Role of institutions in water scarcity
Various institutions are responsible for the proper availability and awareness programs on proper utilization of water. These institutions are not only involved in promulgation of policies but also have active role in provision of water to the masses. During the current survey the sampled population was asked for effectiveness of the mentioned two important roles of these institutions. The survey mainly focused on the tube wells as a source of water supply. It was found that 181 (45.25%) of the total sample respondents agreed that institutions have active role in digging tube wells; 161 (40.25%) were thinking that institutions have no active role in this regard whereas, 62 (15.5%) respondents were unaware of the roles of institutions. The results have been shown in Figure 4.
The chi square p value for this data is 0.199 which is greater than the chosen significance level (?=0.05) hence it is concluded that there is no association between the three groups at 0.05 significance level.
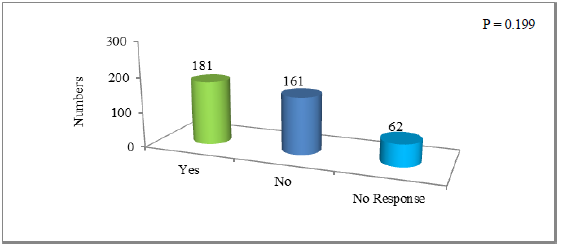
Figure 4: Survey response showing perceptions of people on institutions role in water scarcity.
The perception of sampled population on the effectiveness of policy for proper water utilization by the institutions has been reported in Figure 5. The figure elaborates that only 128 (32.0%) respondents have agreed on institution policies, 229 (57.25%) did not agreed whereas, 43 (10.75%) were with no response. The chi square p value for this data is 0.199 which is greater than the chosen significance level (?=0.05) hence it is concluded that there is no association between the three groups at 0.05 significance level.
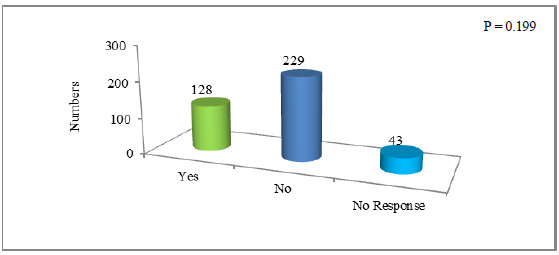
Figure 5: Survey response showing perceptions of people on effectiveness of institutions policies on proper utilization of water.
In order to further elaborate the role of institutions in the water management activities the current survey also focused on the sources of irrigation. The effectiveness of policies and water management activities by the institutions could be easily assessed by the data on sources of irrigation in the study population as presented in Figure 6. The results show that 373 (93.3%) of the study population use tube wells as a source of irrigation, 8 (2%) use crezes whereas, 19 (4.8%) surface and sewerage water. This large number of tube wells digged on public and private level for irrigation has resulted in ground water mining and water scarcity which is a clear evidence of non-effective policies and un-controlled water management by the institutions concerned.
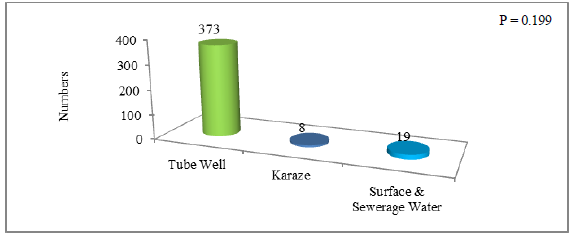
Figure 6: Survey response showing sources of irrigation in sampled population in Quetta Balochistan.
4. Conclusion
The results of the study indicate that the present condition of water in district Quetta is worst. This extremely low level of water cannot fulfill the needs stipulated yearly by household and agricultural production. The water scarcity have badly impacted the society by compelling the population to get away from their native area and to leave their cultivation , adversely affecting the health of population, retarding the promotion of education and threatening the peace and security of the studied population. Similarly water scarcity has adversely affected the economy of the inhabitants of quetta directly due to dryness of tub wells and treas declined land cultivation. The loss in economy due to water shortage has also increased unemployment and enhanced environment pollutants and triggered diseases and health issues. All these findings ask for comprehensive and effective policies promulgation and management activities on the part of related institutions, building of new dams and water reservoirs and more importantly educating the population on proper utilization of water and advocating for follow of regulations about ground water mining.
References
- Halcrow. Supporting Public Resource Management in Balochistan, Basin-wide Water Resources Availability and Use. Irrigation and Power Department, Government of Balochistan, Royal Netherland Government. Halcrow Pakistan (Pvt) in association with Cameos (2007).
- Halcrow. Supporting Public Resource Management in Balochistan, Pishin Lora Basin Management Plan: Final Report. Irrigation and Power Department, Government of Balochistan, Royal Netherland Government. Halcow Pakistan (Pvt) in association with Cameos (2008).
- King N. The Economic Value of Water in South Africa. University of Cape Town Press, Cape Town. (2004): 207-238.
- Louw DB. The Development of a Methodology to Determine the True Value of Water and the Impact of Potential Water Market on the Efficient Utilization of Water in the Berg River Basin. WRC Report (2002): 943/1/02.
- Walter T, Kloos J, Tsegai D. Option for Improving Water Use Efficiency under Worsening Scarcity: evidence from the Middle Olifants Sub-Basin in South Africa. Water SA 37 (2011): 357-370.
- Bhatti SS, Khattak MUK, Roohi R. Planning Water Resource Management in Pishin Lora River Basin of Balochistan Using GIS/RS Techniques.Proceeding of ICAST 2 (2008): 91-97.
- Bajoi AH. Report on reorganization of Agriculture Research and Extension Balochistan University of Information Technology Engineering and Management Sciences Quetta (2004).
- Shah TC, Scott A, Kishore A, et al. Energy-Irrigaiton Nexus in South Asia: Approach to agrarian prosperity with viable power industry. International Water Management Institure (IWMI), India (2002).
- Nasurullah Kha MA, Maqsood A, Malghani MGK, et al. Socio Economic Effect of Water Scarcity in Tehsil Karezat District Pishin Balochistan. Journal of Applied & Emerging Science 2 (2011).
- Khair SM, Culas RJ, Hafeez M. The Causes of Ground Water Decline in Upland Balochistan Region of Pakistan: Implication for Water Management Policies. Paper Presented at the 39th Australian Conference of Economists (2010): 27-29.
- Arkin H, Colton R. Table for the statistics. New York: Barnes and Noble Publication (1963).
- Zainuddin K, Maqsood AK, Zubair MK. Farmers perceptions on impact of water scarcity in Pishin Lora Basin of Balochistan. Pure Appl Biol 6 (2017): 293-303.
Citation: Sadia Barrech, Syed Ainuddin, Najeebullah. Multi-Dimensional Implication of Water Scarcity on Inhibitants of District Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan. Journal of Environmental Science and Public Health 2 (2018): 136-143.
