Cutaneous Mycobacterium Gordonae Infection in A Patient with Myelodysplastic Syndrome
Article Information
Rocco De Pasquale1, Alice Ramondetta1, Roberta Fassari1, Sebastiano Fabio Garozzo2, Laura Scuderi3
1U.O.C. Dermatologia, A.O.U. Policlinico - San Marco, Università degli studi di Catania, Catania, Italy
2U.O.C Patologia Clinica e Biologia Molecolare Clinica P.O Garibaldi Centro, Catania, Italy
3Private practiotioner, Catania, Italy
*Corresponding Author: Rocco De Pasquale, U.O.C. Dermatologia, A.O.U. Policlinico – San Marco, Università degli studi di Catania, Viale Carlo Azeglio Ciampi, 95121, Catania, Italy
Received: 14 April 2021; Accepted: 28 April 2021; Published: 14 May 2021
Citation: Rocco De Pasquale, Alice Ramondetta, Roberta Fassari, Sebastiano Fabio Garozzo, Laura Scuderi. Cutaneous Mycobacterium Gordonae Infection in A Patient with Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports 5 (2021): 422-426.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookKeywords
Cutaneous mycobacterium; Gordonae Infection; Myelodysplastic Syndrome
Cutaneous mycobacterium articles; Gordonae Infection articles; Myelodysplastic Syndrome articles
Cutaneous mycobacterium articles Cutaneous mycobacterium Research articles Cutaneous mycobacterium review articles Cutaneous mycobacterium PubMed articles Cutaneous mycobacterium PubMed Central articles Cutaneous mycobacterium 2023 articles Cutaneous mycobacterium 2024 articles Cutaneous mycobacterium Scopus articles Cutaneous mycobacterium impact factor journals Cutaneous mycobacterium Scopus journals Cutaneous mycobacterium PubMed journals Cutaneous mycobacterium medical journals Cutaneous mycobacterium free journals Cutaneous mycobacterium best journals Cutaneous mycobacterium top journals Cutaneous mycobacterium free medical journals Cutaneous mycobacterium famous journals Cutaneous mycobacterium Google Scholar indexed journals Gordonae Infection articles Gordonae Infection Research articles Gordonae Infection review articles Gordonae Infection PubMed articles Gordonae Infection PubMed Central articles Gordonae Infection 2023 articles Gordonae Infection 2024 articles Gordonae Infection Scopus articles Gordonae Infection impact factor journals Gordonae Infection Scopus journals Gordonae Infection PubMed journals Gordonae Infection medical journals Gordonae Infection free journals Gordonae Infection best journals Gordonae Infection top journals Gordonae Infection free medical journals Gordonae Infection famous journals Gordonae Infection Google Scholar indexed journals ultrasound articles ultrasound Research articles ultrasound review articles ultrasound PubMed articles ultrasound PubMed Central articles ultrasound 2023 articles ultrasound 2024 articles ultrasound Scopus articles ultrasound impact factor journals ultrasound Scopus journals ultrasound PubMed journals ultrasound medical journals ultrasound free journals ultrasound best journals ultrasound top journals ultrasound free medical journals ultrasound famous journals ultrasound Google Scholar indexed journals laparoscopic articles laparoscopic Research articles laparoscopic review articles laparoscopic PubMed articles laparoscopic PubMed Central articles laparoscopic 2023 articles laparoscopic 2024 articles laparoscopic Scopus articles laparoscopic impact factor journals laparoscopic Scopus journals laparoscopic PubMed journals laparoscopic medical journals laparoscopic free journals laparoscopic best journals laparoscopic top journals laparoscopic free medical journals laparoscopic famous journals laparoscopic Google Scholar indexed journals Myelodysplastic Syndrome articles Myelodysplastic Syndrome Research articles Myelodysplastic Syndrome review articles Myelodysplastic Syndrome PubMed articles Myelodysplastic Syndrome PubMed Central articles Myelodysplastic Syndrome 2023 articles Myelodysplastic Syndrome 2024 articles Myelodysplastic Syndrome Scopus articles Myelodysplastic Syndrome impact factor journals Myelodysplastic Syndrome Scopus journals Myelodysplastic Syndrome PubMed journals Myelodysplastic Syndrome medical journals Myelodysplastic Syndrome free journals Myelodysplastic Syndrome best journals Myelodysplastic Syndrome top journals Myelodysplastic Syndrome free medical journals Myelodysplastic Syndrome famous journals Myelodysplastic Syndrome Google Scholar indexed journals treatment articles treatment Research articles treatment review articles treatment PubMed articles treatment PubMed Central articles treatment 2023 articles treatment 2024 articles treatment Scopus articles treatment impact factor journals treatment Scopus journals treatment PubMed journals treatment medical journals treatment free journals treatment best journals treatment top journals treatment free medical journals treatment famous journals treatment Google Scholar indexed journals CT articles CT Research articles CT review articles CT PubMed articles CT PubMed Central articles CT 2023 articles CT 2024 articles CT Scopus articles CT impact factor journals CT Scopus journals CT PubMed journals CT medical journals CT free journals CT best journals CT top journals CT free medical journals CT famous journals CT Google Scholar indexed journals Case Report articles Case Report Research articles Case Report review articles Case Report PubMed articles Case Report PubMed Central articles Case Report 2023 articles Case Report 2024 articles Case Report Scopus articles Case Report impact factor journals Case Report Scopus journals Case Report PubMed journals Case Report medical journals Case Report free journals Case Report best journals Case Report top journals Case Report free medical journals Case Report famous journals Case Report Google Scholar indexed journals Cancer articles Cancer Research articles Cancer review articles Cancer PubMed articles Cancer PubMed Central articles Cancer 2023 articles Cancer 2024 articles Cancer Scopus articles Cancer impact factor journals Cancer Scopus journals Cancer PubMed journals Cancer medical journals Cancer free journals Cancer best journals Cancer top journals Cancer free medical journals Cancer famous journals Cancer Google Scholar indexed journals Syndrome articles Syndrome Research articles Syndrome review articles Syndrome PubMed articles Syndrome PubMed Central articles Syndrome 2023 articles Syndrome 2024 articles Syndrome Scopus articles Syndrome impact factor journals Syndrome Scopus journals Syndrome PubMed journals Syndrome medical journals Syndrome free journals Syndrome best journals Syndrome top journals Syndrome free medical journals Syndrome famous journals Syndrome Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
Introduction
A 78 year-old Caucasian male patient, presented to the Dermatology Unit of San Marco Hospital in Catania following the appearance for about one year of both erythematous-papular lesions tending to confluence in plaque and nodular ones were observed, in correspondence of the back of the hands and fingers and on the left ear helix. These lesions showed red-purple colour, scaling sharp slightly raised borders, and dimensions between 0.5 and 5 cm diameter; the largest ones also showed central resolution and atrophy.
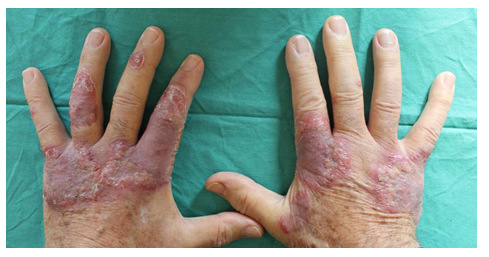
Figure 1: In correspondence of the back of the hands and fingers of a 78-year old male patient, we observe erythematous-papular lesions tending to confluence in plaque and nodular lesions of red-purple colour, scaling sharp slightly raised borders, and dimensions between 0.5 and 5 cm diameter; the largest plaques also showed central resolution and atrophy.
During the previous months he had undergone topical steroid and systemic antibiotic therapy, without any benefit. His medical history was notable for myelodysplastic syndrome.
2. Methods
A cutaneous 5 mm punch biopsy of a nodular lesion from the back of the left hand and routine blood chemistry tests were performed. Histological exam of the hematoxylin and eosin stain revealed hyperkeratotic hyperplastic epidermis with scaly-crust and foci of spongiosis, angiectasias in the dermis, intense inflammatory lymphoplasmacytic and abscessualizing granulocytic infiltrate, with plurinuclear giant cells and foci of collagen necrosis. Outbreaks of granulocyte exocytosis on the follicular epithelium and epidermis were also noticed. In conclusion, the histological finding was compatible with the diagnosis of abscessualizing granulomatous dermatitis with foci of collagen necrosis.
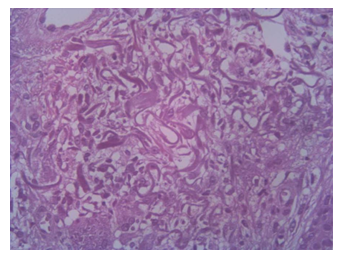
Figure 2: H&E stained longitudinal section obtained from a 5 mm punch biopsy of a nodular lesion from the back of the left hand: hyperkeratotic hyperplastic epidermis with scaly-crust and foci of spongiosis, angiectasias in the dermis, intense inflammatory lymphoplasmacytic and abscessualizing granulocytic, with plurinuclear giant cells and foci of collagen necrosis, outbreaks of granulocyte exocytosis on the follicular epithelium and epidermis.
Anemia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia in accordance with the underlying hematological disorder were detected. Liver enzymes were normal (GOT 12 U/I and GPT 10 U/I) and creatinine values were 1,03 mg/dl. An HIV test was performed, and the result was negative. Chest X-ray showed a mild interstitial reinforcement of the bilateral ilo-paracardiac broncho-vasal weft, a normal cardiac shadow and free cost-phrenic breasts.
3. Results
Biochemical analysis of tissue samples, performed through the extraction of the genomic material with the QIAamp DSP DNA FFPE Tissue kit, the amplification of the genomic material with the Anuplex plus method MTB / NTM Real-Time PCR detection, and the genotyping of mycobacteria with the Genotype Mycobacterium CM VER 2.0 test, highlighted the presence of M. gordonae. Then, in the light of clinical, laboratory and instrumental data, the patient was diagnosed with M. gordonae infection.
After diagnosis, the patient was treated with a combined therapy of Clarithromycin (500 mg PO daily), Ethambutol (1200 mg PO daily), Rifabutin (600 mg PO daily), Fusidic acid + betamethasone valerate cream (twice daily). The skin lesions were completely resolved after 6 months of treatment.
Mycobacterium gordonae, isolated from sputum of patients, is a rare Nontubercular Mycobacterium named after Ruth E. Gordon, who isolated it in 1962. In the past, it was simply considered a non-pathogenic water contaminant [1, 2], while nowadays it is commonly associated with environmental contamination of organic samples. In fact, M. gordonae has been isolated from gastric fluid, urine and mucous membrane swabs collected from healthy patients [3]. Over the years, it has been found that Mycobacterium is responsible for cutaneous and non-cutaneous infections in both immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients [4].
Furthermore, the diagnosis has been certified from the patient’s testimony that affirmed to have had the first cutaneous events after working in the fields. As the literature shows, it has been hypothesized that the lesion on the helix was due to autoinoculation, as the patient was accustomed to touch his ear very often. To the best of our knowledge, the case reported is the third documented case of cutaneous infection from M. gordonae in Italy [5, 6].
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, the infection with M. gordonae can be particularly difficult to diagnose, as it is first of all a very rare disease and furthermore, in-depth and very detailed histological and microbiological investigations are necessary; finally long periods are needed for growth and identification of the isolates.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Funding
The authors report no involvement in the research by the sponsor that could have influenced the outcome of this work.
Authors’ Contributions
All authors have participated to drafting the manuscript, Prof. Rocco De Pasquale revised it critically. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
References
- Ustinova V, et al. First Draft Genome Sequence of a Mycobacterium gordonae Clinical Isolate. Genome announcements 4 (2016): e00638-16.
- Chung J, Ince D, Ford BA, Wanat KA. Cutaneous Infections Due to Nontuberculosis Mycobacterium: Recognition and Management. Am J Clin Dermatol 19 (2018): 867-878.
- Arnow PM, Bakir M, Thompson K, et al. Endemic contamination of clinical specimens by Mycobacterium gordonae. Clin Infect Dis 31 (2000): 472-476.
- Lee, Martin WT et al. Mycobacterium gordonae-associated skin infection in an immunocompetent patient. The Australasian journal of dermatology 59 (2018): e282-e283.
- Foti C, Sforza V, Rizzo C, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of Mycobacterium gordonae infection described for the first time in Italy: a case report. Cases J 2 (2009): 6828.
- Rusconi S, Gori A, Vago L, et al. Cutaneous infection caused by Mycobacterium gordonae in a human immunodeficiency virus-infected patient receiving antimycobacterial treatment. Clin Infect Dis 25 (1997): 1490-1491.
