Comparison of Bis-Plus-D and API 20 Strep for the Identification of Streptococci in the Laboratory of the University Hospital of Befelatanana Antananarivo Madagascar
Article Information
Zafindrasoa Domoina Rakotovao-Ravahatra1*, Jimmy Anders Antilahy1, Joely Nirina Rakotovao-Ravahatra2, Andriamiadana Luc Rakotovao1
1Laboratory of the University Hospital of Befelatanana, Medical Biology Department, Faculty of Medicine, University of Antananarivo, Madagascar
2Doctoral School “Engineering of Industrial, Agricultural and Food Processes and Systems”, Graduate School of Agronomic Sciences, University of Antananarivo, Madagascar
*Corresponding Author: Zafindrasoa Domoina Rakotovao-Ravahatra Laboratory of the University Hospital of Befelatanana, Antananarivo, Madagascar.
Received: 17 September 2022; Accepted: 23 September 2022; Published: 11 October 2022
Citation: Zafindrasoa Domoina Rakotovao-Ravahatra, Jimmy Anders Antilahy, Joely Nirina Rakotovao-Ravahatra, Andriamiadana Luc Rakotovao. Comparison of Bis-Plus-D and API 20 Strep for the identification of streptococci in the Laboratory of the University Hospital of Befelatanana Antananarivo Madagascar. Journal of Analytical Techniques and Research 4 (2022): 130-134.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
Background: In medical analysis laboratories, techniques for identifying bacteria are currently becoming more and more numerous. The objective of this study is to compare the Bis-Plus-D and the API 20 Strep for the identification of streptococci
Methods: During the study period, 22 Gram-positive coci isolates were identified using Api 20 Strep and Bis-Plus-D.
Results: During the study period, 22 isolates of streptococci were identified simultaneously using Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep. The streptococci identified were represented by Streptococcus anginosus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus uberis, Enterococcus columbae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus constellatus, Enterococcus durans Enterococcus casseliflavus, Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. This study showed 50% of discordant results between Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep. Regarding the bacterial identification qualities, they were all excellent (100%) for Api 20 Strep. For Bis-Plus-D, the identification qualities were excellent for 36.4% of bacteria, very good for 36.4% of bacteria, good for 22.7% of bacteria and intermediate for 4.5% of bacteria. Concerning the probability scores for exact identification of bacteria, they vary between 82% to 100% for Api 20 Strep and between 62.6% to 99.9% for Bis-Plus-D.
Conclusion: Api 20 Strep remains the best identification bacterial system and can be used by all bacteriology laboratories for good identification of bacterial species.
Keywords
Bacteria; bacterial identification system; qualitative evaluation
Bacteria articles; bacterial identification system articles; qualitative evaluation articles
Bacteria articles Bacteria Research articles Bacteria review articles Bacteria PubMed articles Bacteria PubMed Central articles Bacteria 2023 articles Bacteria 2024 articles Bacteria Scopus articles Bacteria impact factor journals Bacteria Scopus journals Bacteria PubMed journals Bacteria medical journals Bacteria free journals Bacteria best journals Bacteria top journals Bacteria free medical journals Bacteria famous journals Bacteria Google Scholar indexed journals bacterial identification system articles bacterial identification system Research articles bacterial identification system review articles bacterial identification system PubMed articles bacterial identification system PubMed Central articles bacterial identification system 2023 articles bacterial identification system 2024 articles bacterial identification system Scopus articles bacterial identification system impact factor journals bacterial identification system Scopus journals bacterial identification system PubMed journals bacterial identification system medical journals bacterial identification system free journals bacterial identification system best journals bacterial identification system top journals bacterial identification system free medical journals bacterial identification system famous journals bacterial identification system Google Scholar indexed journals qualitative evaluation articles qualitative evaluation Research articles qualitative evaluation review articles qualitative evaluation PubMed articles qualitative evaluation PubMed Central articles qualitative evaluation 2023 articles qualitative evaluation 2024 articles qualitative evaluation Scopus articles qualitative evaluation impact factor journals qualitative evaluation Scopus journals qualitative evaluation PubMed journals qualitative evaluation medical journals qualitative evaluation free journals qualitative evaluation best journals qualitative evaluation top journals qualitative evaluation free medical journals qualitative evaluation famous journals qualitative evaluation Google Scholar indexed journals streptococci articles streptococci Research articles streptococci review articles streptococci PubMed articles streptococci PubMed Central articles streptococci 2023 articles streptococci 2024 articles streptococci Scopus articles streptococci impact factor journals streptococci Scopus journals streptococci PubMed journals streptococci medical journals streptococci free journals streptococci best journals streptococci top journals streptococci free medical journals streptococci famous journals streptococci Google Scholar indexed journals techniques articles techniques Research articles techniques review articles techniques PubMed articles techniques PubMed Central articles techniques 2023 articles techniques 2024 articles techniques Scopus articles techniques impact factor journals techniques Scopus journals techniques PubMed journals techniques medical journals techniques free journals techniques best journals techniques top journals techniques free medical journals techniques famous journals techniques Google Scholar indexed journals Streptococcus anginosus articles Streptococcus anginosus Research articles Streptococcus anginosus review articles Streptococcus anginosus PubMed articles Streptococcus anginosus PubMed Central articles Streptococcus anginosus 2023 articles Streptococcus anginosus 2024 articles Streptococcus anginosus Scopus articles Streptococcus anginosus impact factor journals Streptococcus anginosus Scopus journals Streptococcus anginosus PubMed journals Streptococcus anginosus medical journals Streptococcus anginosus free journals Streptococcus anginosus best journals Streptococcus anginosus top journals Streptococcus anginosus free medical journals Streptococcus anginosus famous journals Streptococcus anginosus Google Scholar indexed journals Streptococcus agalactiae articles Streptococcus agalactiae Research articles Streptococcus agalactiae review articles Streptococcus agalactiae PubMed articles Streptococcus agalactiae PubMed Central articles Streptococcus agalactiae 2023 articles Streptococcus agalactiae 2024 articles Streptococcus agalactiae Scopus articles Streptococcus agalactiae impact factor journals Streptococcus agalactiae Scopus journals Streptococcus agalactiae PubMed journals Streptococcus agalactiae medical journals Streptococcus agalactiae free journals Streptococcus agalactiae best journals Streptococcus agalactiae top journals Streptococcus agalactiae free medical journals Streptococcus agalactiae famous journals Streptococcus agalactiae Google Scholar indexed journals Streptococcus uberis articles Streptococcus uberis Research articles Streptococcus uberis review articles Streptococcus uberis PubMed articles Streptococcus uberis PubMed Central articles Streptococcus uberis 2023 articles Streptococcus uberis 2024 articles Streptococcus uberis Scopus articles Streptococcus uberis impact factor journals Streptococcus uberis Scopus journals Streptococcus uberis PubMed journals Streptococcus uberis medical journals Streptococcus uberis free journals Streptococcus uberis best journals Streptococcus uberis top journals Streptococcus uberis free medical journals Streptococcus uberis famous journals Streptococcus uberis Google Scholar indexed journals Enterococcus faecalis articles Enterococcus faecalis Research articles Enterococcus faecalis review articles Enterococcus faecalis PubMed articles Enterococcus faecalis PubMed Central articles Enterococcus faecalis 2023 articles Enterococcus faecalis 2024 articles Enterococcus faecalis Scopus articles Enterococcus faecalis impact factor journals Enterococcus faecalis Scopus journals Enterococcus faecalis PubMed journals Enterococcus faecalis medical journals Enterococcus faecalis free journals Enterococcus faecalis best journals Enterococcus faecalis top journals Enterococcus faecalis free medical journals Enterococcus faecalis famous journals Enterococcus faecalis Google Scholar indexed journals Enterococcus faecium articles Enterococcus faecium Research articles Enterococcus faecium review articles Enterococcus faecium PubMed articles Enterococcus faecium PubMed Central articles Enterococcus faecium 2023 articles Enterococcus faecium 2024 articles Enterococcus faecium Scopus articles Enterococcus faecium impact factor journals Enterococcus faecium Scopus journals Enterococcus faecium PubMed journals Enterococcus faecium medical journals Enterococcus faecium free journals Enterococcus faecium best journals Enterococcus faecium top journals Enterococcus faecium free medical journals Enterococcus faecium famous journals Enterococcus faecium Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
1. Introduction
The heterogeneous genus of streptococci plays an important role in human disease. Streptococci are estimated to cause 700 million human infections each year worldwide, with an estimated total of 500,000 deaths. Louis Pasteur recognized streptococci as one of the first microorganisms to cause contagious disease in 1879 [1]. Most streptococci are commensals, pathogens, or opportunistic pathogens for humans and animals [2]. It is therefore of immense importance to characterize and identify these bacteria. The prognosis of bacterial infections depends not only on the antibiotics used but also by the sensitivity of germs to these antibiotics [3]. The role of microbiology laboratories is to correctly identify streptococci and correctly perform the antibiogram in order to ensure proper management of the patient's infectious disease.
In developing countries like Madagascar, manual bacterial identification systems are still used. The majority of bacteriology laboratories in Madagascar use the Api 20 Strep bacterial identification system to identify the streptococci. However, the use of this kit has some drawbacks. Thus, it was decided to use other bacterial identification systems offered by the suppliers. This is the Bis-Plus-D. Before using the Bis-Plus-D, it must be compared with the Api 20 Strep. Thus, the objective of this study is to compare the 2 bacterial identification systems Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep for the identification of streptococci.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Type and period of study
This is an evaluative study by comparing the two bacterial identification systems Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep over a period of 3 months from January 2022 to March 2022 in the laboratory of the University Hospital of Joseph Raseta Befelatanana.
2.2. Procedures
During the study period, 22 bacterial isolates were identified simultaneously with Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep. Bis-Plus-D is a new bacterial identification system provided by Cypress Diagnostics and should be evaluated before use by comparing it with Api 20 Strep. Indeed, since the opening of the bacteriology laboratory of the University Hospital of Joseph Raseta Befelatanana. The Api brand bacterial identification systems supplied by Biomérieux have been the only ones to be used in the laboratory. Thus, Api 20 Strep represents the gold standard test in this study.
API reagent include 25 microtubes containing dehydrated substrates. Conventional tests are inoculated with a saline bacterial suspension which replenishes the media. The reactions produced during the incubation period are reflected by spontaneous color changes or revealed by the addition of reagents. The assimilation tests are inoculated with a minimum medium and the bacteria grow only if they are able to use the corresponding substrate. During incubation, metabolism produces color changes that are either spontaneous or revealed by the addition of reagents. The reactions are read according to theReading Table and the identification is obtained by referring to the Analytical Profile Index or using the identification software. API 20 Strep is a standardized system combining 20 biochemical tests which have a high discriminating power. It makes it possible to make a group or species diagnosis for most streptococci, enterococci and for the most common related germs.
Concerning the Bis-Plus-D, its panel is made of 24 microtiter wells, each of them with different dehydrated reagents for a specific biochemistry test. Upon addition of bacterial suspension, the reagents in the well are constituted. During incubation, the metabolic activity of the inoculated bacteria is coupled to a certain colorimetric reaction depending on the specific test. A supplementary color code guide allows the user to determine whether every test is positive or negative. This, in last instance, depends on whether the bacteria from the inoculum possess or not a certain metabolic activity. Based on the acquired results profile, the identification of the bacterial species can be obtained by introducing the results profile in the Cypress identification software.
2.3. Study parameters
Study parameters were represented by bacteriological results on Bis-Plus-D, bacteriological results on API 20 Strep, the probability scores of exact identification of the bacterial species, the identifying qualities of streptococci, the concordance and discordance of the results, advantages and disadvantages of using Bis-Plus-D and API 20 Strep.
2.4. Ethical considerations
This study was authorized by the director of establishment of the University Hospital of Befelatanana and the Department Head of the laboratory before its implementation. This study respected the notion of anonymity and confidentiality. Otherwise, this study was carried out with the technical and financial support of the company Médical International of Madagascar and the Mérieux Foundation.
3. Results
3.1. Bacteria identified by Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep during the study period
During the study period, 22 isolates of streptococci were identified simultaneously using Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep. The streptococci identified were represented by Streptococcus anginosus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus uberis, Enterococcus columbae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus constellatus, Enterococcus durans Enterococcus casseliflavus, Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium (table 1).
|
Bacteria identified |
Bis-Plus-D |
API 20 Strep |
Results |
|
bacteria 1 |
Enterococcus columbae |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Discordance |
|
bacteria 2 |
Streptococcus pyogenes |
Streptococcus anginosus |
Discordance |
|
bacteria 3 |
Streptococcus constellatus |
Streptococcus agalactiae |
Discordance |
|
bacteria 4 |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Concordance |
|
bacteria 5 |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Concordance |
|
bacteria 6 |
Enterococcus durans |
Enterococcus faecium |
Discordance |
|
bacteria 7 |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Concordance |
|
bacteria 8 |
Enterococcus durans |
Enterococcus faecium |
Discordance |
|
bacteria 9 |
Streptococcus agalactiae |
Streptococcus agalactiae |
Concordance |
|
bacteria 10 |
Enterococcus faecium |
Enterococcus faecium |
Concordance |
|
bacteria 11 |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Concordance |
|
bacteria 12 |
Enterococcus faecium |
Enterococcus faecium |
Concordance |
|
bacteria 13 |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Concordance |
|
bacteria 14 |
Enterococcus faecium |
Enterococcus faecium |
Concordance |
|
bacteria 15 |
Enterococcus casseliflavus |
Streptococcus uberis |
Discordance |
|
bacteria 16 |
Enterococcus casseliflavus |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Discordance |
|
bacteria 17 |
Enterococcus casseliflavus |
Enterococcus faecium |
Discordance |
|
bacteria 18 |
Enterococcus casseliflavus |
Enterococcus faecium |
Discordance |
|
bacteria 19 |
Enterococcus faecium |
Enterococcus faecium |
Concordance |
|
bacteria 20 |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Concordance |
|
bacteria 21 |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Enterococcus faecium |
Discordance |
|
bacteria 22 |
Enterococcus faecalis |
Enterococcus faecium |
Discordance |
Table 1: Bacteria identified by Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep
This study showed 50% of discordant results between Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep (figure 1)
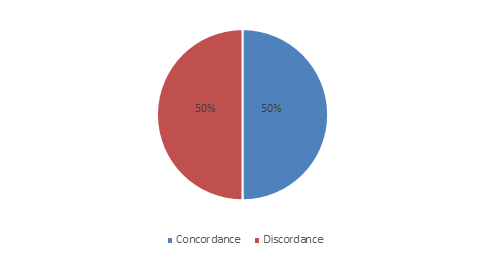
Figure 1: Concordance and discordance of Bis-Plus-D et Api 20 Strep results
3.2. Bacterial identification qualities
Regarding the bacterial identification qualities, they were all excellent (100%) for Api 20 Strep. For Bis-Plus-D, the identification qualities were excellent for 36.4% of bacteria, very good for 36.4% of bacteria, good for 22.7% of bacteria and intermediate for 4.5% of bacteria (figure 2).
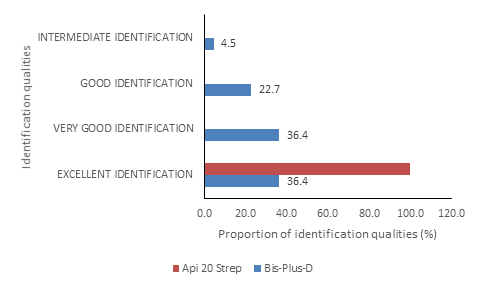
Figure 2: Bacterial Identification qualities of Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep
3.3. Probability scores for exact identification of bacteria
Concerning the probability scores for exact identification of bacteria, they vary between 82%
to 100% for Api 20 Strep and between 62.6% to 99.9% for Bis-Plus-D (figure 3).
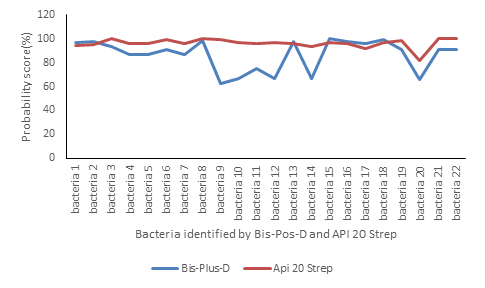
Figure 3: Probability scores for exact identification of bacteria by Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep
3.4. Advantages and Disadvantages of using Api 20 Strep and Bis-Plus-D
The advantages and disadvantages of using Api 20 Strep and Bis-Pos-D are detailed in (table 2).
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
Bis-Plus-D |
Lasting expiration date |
|
|
The price is cheaper in the trade |
Need for several additional tests |
|
|
Identifies of all Gram-positive cocci, corynebacteria and anaerobes |
Sometimes probability score less than 80% |
|
|
Api 20 Strep |
No need for additional tests |
Short expiration date |
|
Probability score greater than 90% |
The price is more expensive in the trade |
|
|
Cannot identifies all Gram positive cocci but only the streptococci |
||
|
Cannot identifies corynebacteria and anaerobes |
Table 2: Advantages and disadvantages of using api 20 Strep and Bis-Plus-D
4. Discussion
Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep systems are both bacterial identification systems. In this study, we identified 22 bacteria using Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep. The 22 bacteria had the bacteriological characteristics of streptococci and enterococci, i.e. Gram-positive and catalase-negative cocci.
Concerning the results, half of the bacterial identification results were discordant between Bis-Plus-D and Api 20 Strep. Thus, it is necessary to analyze which of the 2 tests is the most reliable.
Regarding the bacterial identification qualities, they were all excellent (100%) for Api 20 Strep versus 36.4% for Bis-Plus-D. We can already see from this result that the Api 20 Strep test is more reliable than the Bis-Plus-D test. Similarly, looking at the probability scores of the 2 tests, those of the API 20 E are higher and some of these scores even reach 100%. Thus, all the results of this study showed that API 20 E is the best test for the identification of streptococci and enterococci. Nevertheless, it cannot be concluded that Bis-Plus-D is unreliable. Indeed, the identification process consists of recognizing an unknown bacterium by defining its membership in a species. It is based on the choice of a set of biochemical tests carried out by specific software. This set constitutes an identification kit. Depending on the response profile observed, a probability of belonging to each species is calculated. We retain the most probable species. A probability score between 60 and 100% means that the confidence level is high and therefore the identification is reliable. For a score <60% the level of confidence is low, the software then proposing between two and four identifications [4-7]. In this study, all Bis-Plus-D probability scores were above 60% showing that this test is also reliable.
Furthermore, even though this study found that Api 20 Strep is more reliable than Bis-Plus-D, there are some disadvantages of using the Api 20 Strep. First, the expiry date of the kits does not exceed one year when they arrive at the laboratory. Second, the kit can only identify streptococci. Third, Third, Api 20E costs more expensive than Bis-Plus-D [8]. On the other hand, the use of Bis-Plus-D has many advantages. First, the kit has an expiration date of two to three years when it arrives at the laboratory. Secondly, the kit can identify all Gram-positive cocci, corynebacteria and anaerobes without exception. Third, the kit costs less than the API kits [9].
At the end of this study, we can conclude that the API 20 Strep test is the best test in the identification of streptococci and enterococci because its bacterial identification qualities are all excellent and its probability scores for exact identification of bacteria sometimes reach 100%.
Thus, the results of this study allow us to make some recommendations. First, Cypress Diagnostics should review the reagents contained in the Bis-Plus-D kit if there are any reagents that need to be added or changed to increase the reliability of the results. Secondly, large city laboratories that receive a lot of bacteriological analyzes should use the Api 20 Strep bacterial identification system as they can purchase it annually and the rapid expiry of this test is not a problem for them as well as the cost of the test. On the other hand, it is preferable that the small laboratories which do not do a lot of bacteriological analyze use the Bis-Plus-D because its expiry date is long, and its price is cheaper on the market. Likewise, the small laboratory does not need to buy other bacterial identification systems for the identification of other bacilli (corynebacteria and anaerobes) because the Bis-Plus-D is sufficient to identify them all.
In brief, the proper observance of standard operating procedures for each type of bacterial identification system should be carried out for performs a good bacterial identification in order to obtain the best probability score which is 100%.
Conclusion
Api 20 Strep remains the best identification bacterial system. However, after a review of the kit by Cypress Diagnostics, Bis-Plus-D can be used by medical analysis laboratories, especially if these laboratories do not need to perform a lot of bacterial identification tests. The proper observance of standard operating procedures for each type of bacterial identification system should be carried out for performs a good bacterial identification in order to obtain the best probability score which is 100%.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the staff of the laboratory of University Hospital of Befelatanana and all the laboratory technicians. Similarly, we would like to express our gratitude to the director of establishment for authorizing us to carry out this study. And we warmly thank the International Medical Society of Madagascar and the Mérieux Foundation for the technical and financial support during the realization of this study.
Competing interests
Authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
References
- Rohde M, Cleary PP. Adhesion and invasion of Streptococcus pyogenes into host cells and clinical relevance of intracellular streptococci. In: Ferretti J J, Stevens D L, Fischetti V A, editors. Streptococcus pyogenes: Basic Biology to Clinical Manifestations [Internet]. Oklahoma City (OK): University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center (2016).
- Zhang T, Zhu J, Xu J, et al. Regulation of (p)ppGpp and Its Homologs on Environmental Adaptation, Survival, and Pathogenicity of Streptococci. Frontiers Microbiology 11 (2020): 1842.
- Jehl F, Chabaud A, Grillon. L’antibiogramme : diamètres ou CMI ?. Journal des Anti-infectieux 17 (2015): 125-139.
- Chen J H, Ho P L, Kwan G S, et al. Direct bacterial identification in positive blood cultures by use of two commercial matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry systems”. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 51 (2013): 1733-1739.
- Moon J Y, Kim S J, Moon M H, et al. Differential estimation of isomeric 2- and 4-methoxylated estrogens in serum by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical sciences, JSAC 29 (2013):345-351.
- Patel R. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry in clinical microbiology. Clinical infectious diseases, IDSA 57 (2013): 564-572.
- Westblade L F, Jennemann R, Branda J A, et al. Multicenter study evaluating the Vitek MS system for identification of medically important yeasts. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 51 (2013): 2267-2272.
- Api 20E instructions available online at http://biomanufacturing.org
- Bis NEG-D instructions available online at http://diagnostics.be
