Bilateral Lung and Liver Hydatid Cyst with Massive Hydropneumothorax: A Rare Case Report in Kuwait
Article Information
Ahmad E Al-Mulla1*, Derar Al Shehab2, Essa AlGhunaim2, Ehab Saad Imam1, Hamad F Alsanea1
1Department of surgery Farwaniya hospital, Ministry of Health, Kuwait
2Cardiothoracic surgery department thoracic unit, Chest hospital, Ministry of Health, Kuwait
*Corresponding author: Ahmad E Al-Mulla, Department of surgery Farwaniya hospital, Ministry of Health, Kuwait
Received: 13 October 2021; Accepted: 20 October 2021; Published: 21 October 2021
Citation: Ahmad E Al-Mulla, Derar Al Shehab, Essa AlGhunaim, Ehab Saad Imam, Hamad F Alsanea. Bilateral Lung and Liver Hydatid Cyst with Massive Hydropneumothorax: A Rare Case Report in Kuwait. Journal of Surgery and Research 4 (2021): 565-571.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
Bilateral lung and synchronous hydatid cyst is a unique presentation in a patient. It is endemic in some parts of the world, but it is rare in Kuwait. Hydatid cyst results from Echinococcus infection, and it affects between one and nine people in 10,000 countries where it is endemic. Management of hydropneumothorax because of hydatid cyst can proceed in two or one stage, depending on the extent and presentation of the disease. We are presenting the course and management of a 19-year-old male presented with a unique Echinococcus infection.
Keywords
Echinococcus infection, Hydatid cyst, Hydropneumothorax, Synchronous lung and liver cysts
Echinococcus infection articles, Hydatid cyst articles; Hydropneumothorax articles; Synchronous lung and liver cysts articles
Echinococcus infection articles Echinococcus infection Research articles Echinococcus infection review articles Echinococcus infection PubMed articles Echinococcus infection PubMed Central articles Echinococcus infection 2023 articles Echinococcus infection 2024 articles Echinococcus infection Scopus articles Echinococcus infection impact factor journals Echinococcus infection Scopus journals Echinococcus infection PubMed journals Echinococcus infection medical journals Echinococcus infection free journals Echinococcus infection best journals Echinococcus infection top journals Echinococcus infection free medical journals Echinococcus infection famous journals Echinococcus infection Google Scholar indexed journals Hydatid cyst articles Hydatid cyst Research articles Hydatid cyst review articles Hydatid cyst PubMed articles Hydatid cyst PubMed Central articles Hydatid cyst 2023 articles Hydatid cyst 2024 articles Hydatid cyst Scopus articles Hydatid cyst impact factor journals Hydatid cyst Scopus journals Hydatid cyst PubMed journals Hydatid cyst medical journals Hydatid cyst free journals Hydatid cyst best journals Hydatid cyst top journals Hydatid cyst free medical journals Hydatid cyst famous journals Hydatid cyst Google Scholar indexed journals Hydropneumothorax articles Hydropneumothorax Research articles Hydropneumothorax review articles Hydropneumothorax PubMed articles Hydropneumothorax PubMed Central articles Hydropneumothorax 2023 articles Hydropneumothorax 2024 articles Hydropneumothorax Scopus articles Hydropneumothorax impact factor journals Hydropneumothorax Scopus journals Hydropneumothorax PubMed journals Hydropneumothorax medical journals Hydropneumothorax free journals Hydropneumothorax best journals Hydropneumothorax top journals Hydropneumothorax free medical journals Hydropneumothorax famous journals Hydropneumothorax Google Scholar indexed journals Synchronous lung articles Synchronous lung Research articles Synchronous lung review articles Synchronous lung PubMed articles Synchronous lung PubMed Central articles Synchronous lung 2023 articles Synchronous lung 2024 articles Synchronous lung Scopus articles Synchronous lung impact factor journals Synchronous lung Scopus journals Synchronous lung PubMed journals Synchronous lung medical journals Synchronous lung free journals Synchronous lung best journals Synchronous lung top journals Synchronous lung free medical journals Synchronous lung famous journals Synchronous lung Google Scholar indexed journals liver cysts articles liver cysts Research articles liver cysts review articles liver cysts PubMed articles liver cysts PubMed Central articles liver cysts 2023 articles liver cysts 2024 articles liver cysts Scopus articles liver cysts impact factor journals liver cysts Scopus journals liver cysts PubMed journals liver cysts medical journals liver cysts free journals liver cysts best journals liver cysts top journals liver cysts free medical journals liver cysts famous journals liver cysts Google Scholar indexed journals pneumothorax articles pneumothorax Research articles pneumothorax review articles pneumothorax PubMed articles pneumothorax PubMed Central articles pneumothorax 2023 articles pneumothorax 2024 articles pneumothorax Scopus articles pneumothorax impact factor journals pneumothorax Scopus journals pneumothorax PubMed journals pneumothorax medical journals pneumothorax free journals pneumothorax best journals pneumothorax top journals pneumothorax free medical journals pneumothorax famous journals pneumothorax Google Scholar indexed journals surgical excision articles surgical excision Research articles surgical excision review articles surgical excision PubMed articles surgical excision PubMed Central articles surgical excision 2023 articles surgical excision 2024 articles surgical excision Scopus articles surgical excision impact factor journals surgical excision Scopus journals surgical excision PubMed journals surgical excision medical journals surgical excision free journals surgical excision best journals surgical excision top journals surgical excision free medical journals surgical excision famous journals surgical excision Google Scholar indexed journals hydropneumothorax articles hydropneumothorax Research articles hydropneumothorax review articles hydropneumothorax PubMed articles hydropneumothorax PubMed Central articles hydropneumothorax 2023 articles hydropneumothorax 2024 articles hydropneumothorax Scopus articles hydropneumothorax impact factor journals hydropneumothorax Scopus journals hydropneumothorax PubMed journals hydropneumothorax medical journals hydropneumothorax free journals hydropneumothorax best journals hydropneumothorax top journals hydropneumothorax free medical journals hydropneumothorax famous journals hydropneumothorax Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
1. Introduction
A hydatid cyst (HC) is a medical emergency. It is endemic in Africa, Central Asia, southern South America, the Mediterranean, and the Middle East [1]. It affects between one and nine people in 10,000 countries where it is endemic [2]. One of the crucial problems in Echinococcus infection is morbidity in young adults and mortality (2.5-7%) in infected cases [3]. Our case report discusses the management course of a 19-year-old Syrian patient who presented with bilateral lung (HC) with hydropneumothorax with synchronous liver cysts.
2. Case Presentation
A 19-year-old Syrian male presented to our emergency department complaining of a one-day history of sudden right-sided chest pain with dyspnoea, productive cough, nausea, and vomiting. The patient had similar symptoms three months ago after encountering cattle and sheep on his farm and was treated conservatively. Upon examination, he had decreased breath sounds, especially on the right, and hyper-resonance on percussion. A chest x-ray (CXR) showed massive right-sided pneumothorax with bilateral cavitation (Figure 1). The surgical team inserted a 32F chest tube in casualty (Figure 2). He was admitted for further observation and investigation. CT scans of his chest and abdomen were done, demonstrating a sizeable 7 x 6.3 cm complicated cyst lesion with compression on the lower lobe of the right lung and a smaller 1.7 cm adjacent cyst. A 9 x 8 cm cystic lesion at the left lung with another daughter cyst measuring about 0.7 cm were also observed. Another non-enhancing cyst was found on the liver's right lobe, measuring approximately 2.6 x 2.7 cm. The impression was hydropneumothorax with bilateral lung synchronous liver hydatid cyst (Figure 3). Blood and sputum serology was positive for Echinococcus. The patient was referred to chest surgeons and physicians for assessment. They decided to start him on antiparasitic medication for three weeks, followed by surgical excision of the hydatid cysts. A two-stage operation was scheduled at the chest hospital.
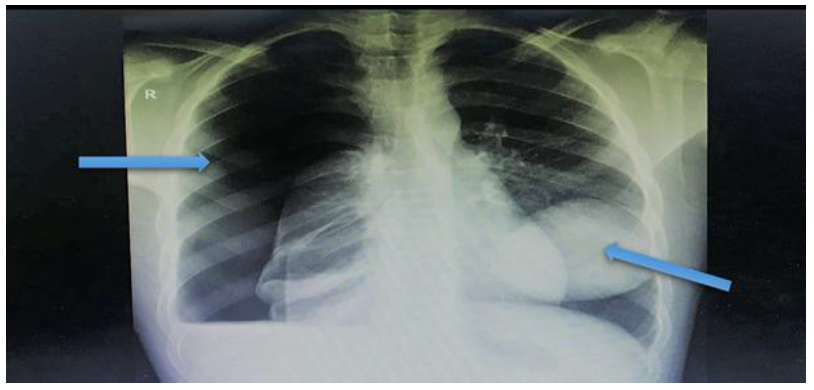
Figure 1: Chest X-ray highlighting a massive right pneumothorax and left hydatid cyst shadow
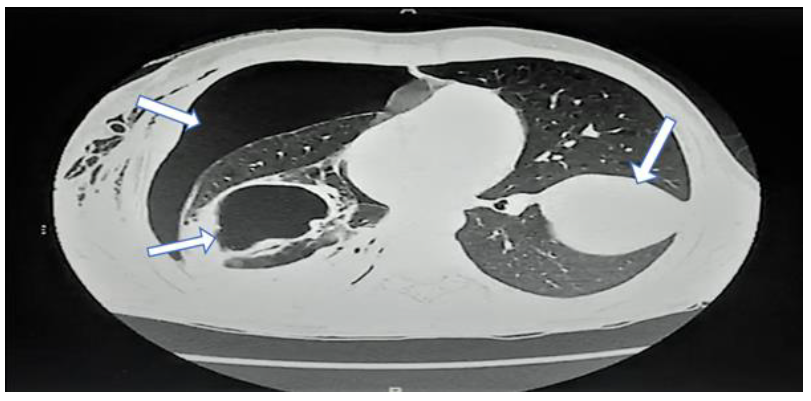
Figure 2: CT-scan lung window demonstrating right-sided pneumothorax and cavitation and a huge left-side cyst.
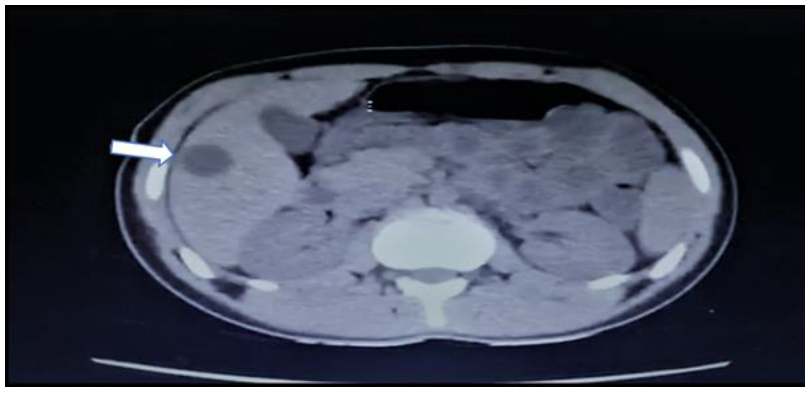
Figure 3: CT-scan abdomen highlighting a cyst on the right lobe of the liver.
2.1 First stage operation
The thoracic team operated in two stages because of the cysts’ sizes and allowed the patient to recover. The first operation was through a right-side thoracotomy incision; a sizable hydatid cyst was excised from the lung, with lobectomy and debridement (Figures 4,5). A chest drain was placed at the site of the operation.
2.2 Post-operative
Recovery in the hospital was uneventful. The patient was discharged after removal of chest drain and completing antibiotics. The patient was scheduled for a second-stage operation after one month.
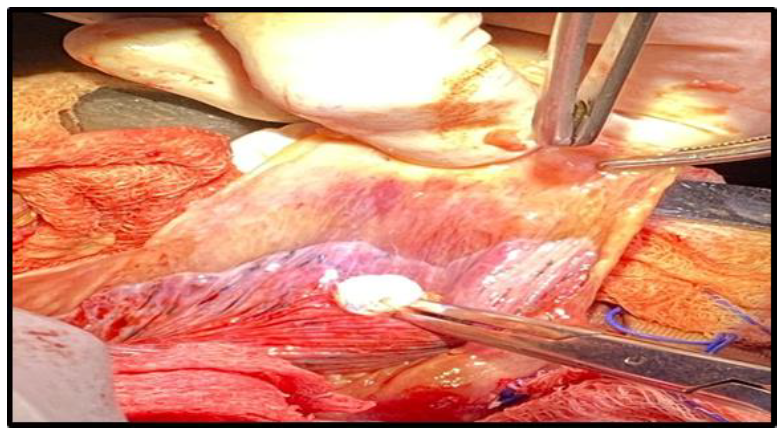
Figure 4: Right-side thoracotomy and extraction of the hydatid cyst.
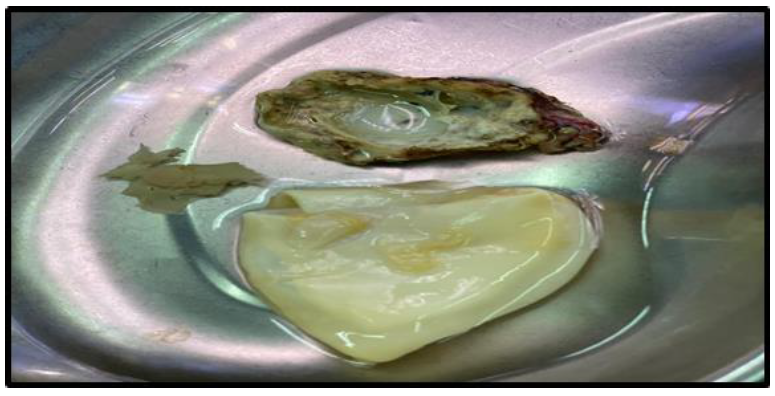
Figure 5: Right-side hydatid cyst with necrotic tissue.
2.3 Second-stage operation
As in the previous approach, a left-side thoracotomy was performed- dissection through dense adhesion. Debridement of necrotic lung tissue, left-side lobectomy, complete cyst extraction and chest drain was fixed (Figures 6,7). The patient had an uneventful recovery in the hospital. He was discharged after chest drain removal and completing antibiotics. The first outpatient visit was scheduled after 14 days. The patient was recovering well, with clean wounds and no complaint. Histopathology showed hydatid cyst and necrotic tissue.
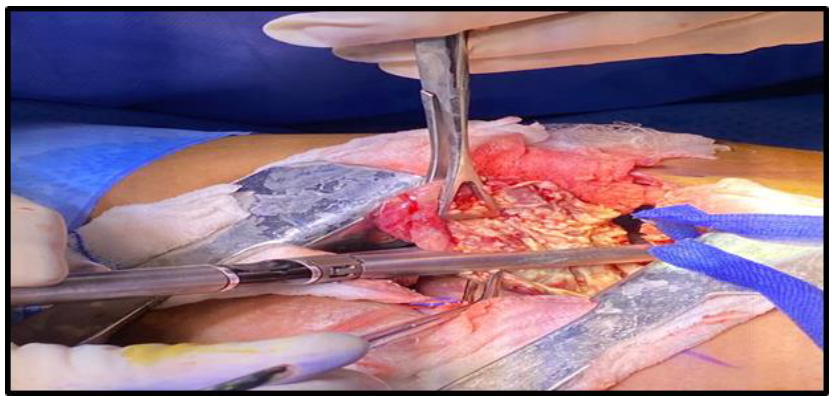
Figure 6: Lobectomy and debridement of necrotic tissue.
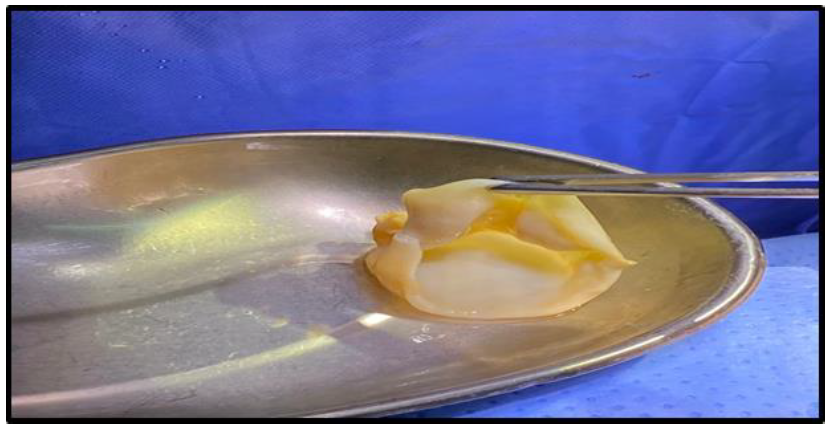
Figure 7: Complete excision of left-side hydatid cyst.
3. Discussion
Hydatid cyst (HC) is a zoonotic disease that occurs worldwide, especially in rearing cattle and farming areas. The two- to a seven-millimetre parasite (embryonated eggs) infects humans through direct ingestion of a tapeworm larva, either from an encounter with a definitive infected host (dogs), intermediate hosts (sheep and cattle) or indirectly by contaminated water or vegetables [4]. There are two types of Echinococcus: granulosus and multilocularis [5]. (HC) can be multiple or solitary and may remain asymptomatic for years only to be discovered accidentally by imaging or present acutely as an abdominal or respiratory manifestation or anaphylactic shock. Most larvae are destroyed in the liver, which acts as a primary filter. 50–75% of cysts are in the liver, 40% in the lungs and the rest are in other organs such as muscles (5%), bones (3%), kidneys (2%), spleen (1%), and the brain (<1%) [6]. The most helpful tools in diagnosing (HC) are ultrasound (USG) and computer tomography scan (CT-scan). Laboratory screening examinations are usually normal; however, when imaging is combined with serological tests, diagnosis is definitive. The diagnosis was achieved with a CT scan and serological test of the blood and sputum [7]. Medical treatment with antiparasitic agents (albendazole) can be used pre-operatively to reduce large cysts, sterilise, prevent spillage and anaphylactic shock during surgery, and eradicate any remnant parasite in the system post-operatively [8]. The Percutaneous Aspiration Injection and Re-aspiration (PAIR) technique, under ultrasound or CT-scan guidance, is an alternative option for patients who refuse or cannot withstand surgery. Nevertheless, surgery is the only possible treatment to remove the cysts and cure [9]. The main principle of surgery is to eradicate the parasite, minimise spillage and obliterate the remnant cavity. Management of lung hydatid cyst primary is surgical excision, which can be achieved in one- or two-stage surgeries with intervals of 3-4 weeks between interventions [10]. A two-stage surgery was favourable because it helps remove multiple small, complicated cysts and aids recovery when lobectomy is required in a patient with a poor cardiopulmonary reserve and chronic medical condition. Recently, one-stage surgery has become the preferred option. A study compared one-stage surgery with the traditional two-stage surgery in 198 patients (1968-2000) and concluded that one-stage surgery is preferable in decreasing morbidity, hospital costs and rapid recovery [2]. Nevertheless, in our case report, the two-stage operation was performed due to the size of the hydatid cysts on both lungs, the presence of extensive necrotic tissue that required debridement and excision, and to give the patient a resting period after major surgery. The minimally invasive approach in pulmonary and hepatic hydatid cysts is becoming more popular. It has a low anaphylactic and spillage rate compared to traditional open surgery, and it also entails a shorter stay in hospital, and it is more cosmetic. It involves aspiration, injection of scolicidal agent, deroofing, removing cysts [11,12].
4. Conclusion
Bilateral lung and synchronous liver hydatid cysts are rare and complicated infections that require a multidisciplinary approach to succeed. Presenting this unique case and management approach is crucial for future medical workers.
Acknowledgement
Special thanks to our head of department, Dr Khalid AL Bassam, and the management at Farwaniya hospital for continuous support in this publication. Also, we would like to extend our appreciation to our colleagues in the thoracic unit at the chest hospital, at Al Sabah Hospital for their fantastic cooperation.
Funding
None required
Conflict of interest
None
References
- Ezer A, Kilic D, Oguzkurt L, et al. Treatment of multiple primary hydatid cysts. Int Surg 93 (2008): 103-106.
- Petrov DB, Terzinacheva PP, Djambazov VI, et al. Surgical treatment of bilateral hydatid disease of the lung. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 19 (2001): 918-923.
- Belhassen-García M, Romero-Alegria A, Velasco-Tirado V, et al. Study of hydatidosis-attributed mortality in endemic area. Plos One 9 (2014): e91342.
- Ammann RW, Eckert J. Cestodes. Echinococcus. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 25 (1996): 655-689
- Babu KS, Goel D, Prayaga A, et al. Intraabdominal hydatid cyst: a case report. Acta Cytol 52 (2008): 464-466.
- Jerry M, Benzarti M, Garrouche A, et al. Hydatid disease of the lungs. Study of 386 cases. Am Rev Respir Dis 146 (1992): 185-189.
- Anadol D, Ozçelik U, Kiper N, et al. Treatment of hydatid disease. Paediatr Drugs 3 (2001): 123-135.
- Aribas BK, Dingil G, Köroglu M et al. Liver Hydatid cyst with transdiaphragmatic rupture and lung hydatid cyst ruptured into bronchi and pleural space. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34 (2011): 260-265.
- WHO Guidelines for treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Bull World Health Organ 74 (1996): 231-242.
- Samala DS, Gedam MC, Gajbhiye R. Laparoscopic management of hydatid cyst of liver with palanivelu hydatid system over a period of 3 years: A case series of 32 patients. The Indian Journal of Surgery 77 (2015): 918-922.
