Bilateral Elastofibroma Dorsi as Differential Diagnosis in Posterior Chest Wall Tumor: A Case Report
Article Information
Frederik Lundgaard Hansen1*, Thomas Stokholm Nørlinger2, Rikke Thorninger1
1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Regional Hospital Randers, Denmark
2Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark
*Corresponding Author: Frederik Lundgaard Hansen, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Regional Hospital Randers, Denmark
Received: 02 February 2020; Accepted: 28 February 2020; Published: 10 March 2020
Citation: Frederik Lundgaard Hansen, Thomas Stokholm Nørlinger, Rikke Thorninger. Bilateral Elastofibroma Dorsi as Differential Diagnosis in Posterior Chest Wall Tumor: A Case Report. Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports 4 (2020): 235-238.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
Elastofibroma dorsi (ED) is a relatively common, albeit rarely diagnosed, benign soft tissue tumor, often with a sub- or infrascapular localization. ED is most common in females >50 years of age, and is unilateral in 67-90% of cases [1]. The pathogenesis is unclear, but it is hypothesized that repeated microtrauma stemming from friction between the scapula and the posterior thoracic wall induces an abnormal proliferation of fibroelastic tissue. Studies have also shown considerable heritability [2]. The condition is often asymptomatic, but can result in pain and decrease in upper extremity function. The diagnosis is made from MRI or pathology examination of a biopsy or tissue post excision. The present paper discusses a case of bilateral ED in a 76 year old female with a history of several years of manual labor as a hairdresser.
Keywords
Tumor; Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi; Tissue tumor
Tumor articles, Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi articles, Tissue tumor articles
Tumor articles Tumor Research articles Tumor review articles Tumor PubMed articles Tumor PubMed Central articles Tumor 2023 articles Tumor 2024 articles Tumor Scopus articles Tumor impact factor journals Tumor Scopus journals Tumor PubMed journals Tumor medical journals Tumor free journals Tumor best journals Tumor top journals Tumor free medical journals Tumor famous journals Tumor Google Scholar indexed journals Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi articles Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi Research articles Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi review articles Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi PubMed articles Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi PubMed Central articles Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi 2023 articles Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi 2024 articles Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi Scopus articles Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi impact factor journals Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi Scopus journals Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi PubMed journals Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi medical journals Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi free journals Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi best journals Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi top journals Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi free medical journals Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi famous journals Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi Google Scholar indexed journals hypertension articles hypertension Research articles hypertension review articles hypertension PubMed articles hypertension PubMed Central articles hypertension 2023 articles hypertension 2024 articles hypertension Scopus articles hypertension impact factor journals hypertension Scopus journals hypertension PubMed journals hypertension medical journals hypertension free journals hypertension best journals hypertension top journals hypertension free medical journals hypertension famous journals hypertension Google Scholar indexed journals Tissue tumor articles Tissue tumor Research articles Tissue tumor review articles Tissue tumor PubMed articles Tissue tumor PubMed Central articles Tissue tumor 2023 articles Tissue tumor 2024 articles Tissue tumor Scopus articles Tissue tumor impact factor journals Tissue tumor Scopus journals Tissue tumor PubMed journals Tissue tumor medical journals Tissue tumor free journals Tissue tumor best journals Tissue tumor top journals Tissue tumor free medical journals Tissue tumor famous journals Tissue tumor Google Scholar indexed journals Chromosomes articles Chromosomes Research articles Chromosomes review articles Chromosomes PubMed articles Chromosomes PubMed Central articles Chromosomes 2023 articles Chromosomes 2024 articles Chromosomes Scopus articles Chromosomes impact factor journals Chromosomes Scopus journals Chromosomes PubMed journals Chromosomes medical journals Chromosomes free journals Chromosomes best journals Chromosomes top journals Chromosomes free medical journals Chromosomes famous journals Chromosomes Google Scholar indexed journals treatment articles treatment Research articles treatment review articles treatment PubMed articles treatment PubMed Central articles treatment 2023 articles treatment 2024 articles treatment Scopus articles treatment impact factor journals treatment Scopus journals treatment PubMed journals treatment medical journals treatment free journals treatment best journals treatment top journals treatment free medical journals treatment famous journals treatment Google Scholar indexed journals Elastofibroma dorsi articles Elastofibroma dorsi Research articles Elastofibroma dorsi review articles Elastofibroma dorsi PubMed articles Elastofibroma dorsi PubMed Central articles Elastofibroma dorsi 2023 articles Elastofibroma dorsi 2024 articles Elastofibroma dorsi Scopus articles Elastofibroma dorsi impact factor journals Elastofibroma dorsi Scopus journals Elastofibroma dorsi PubMed journals Elastofibroma dorsi medical journals Elastofibroma dorsi free journals Elastofibroma dorsi best journals Elastofibroma dorsi top journals Elastofibroma dorsi free medical journals Elastofibroma dorsi famous journals Elastofibroma dorsi Google Scholar indexed journals kidney articles kidney Research articles kidney review articles kidney PubMed articles kidney PubMed Central articles kidney 2023 articles kidney 2024 articles kidney Scopus articles kidney impact factor journals kidney Scopus journals kidney PubMed journals kidney medical journals kidney free journals kidney best journals kidney top journals kidney free medical journals kidney famous journals kidney Google Scholar indexed journals heart surgery articles heart surgery Research articles heart surgery review articles heart surgery PubMed articles heart surgery PubMed Central articles heart surgery 2023 articles heart surgery 2024 articles heart surgery Scopus articles heart surgery impact factor journals heart surgery Scopus journals heart surgery PubMed journals heart surgery medical journals heart surgery free journals heart surgery best journals heart surgery top journals heart surgery free medical journals heart surgery famous journals heart surgery Google Scholar indexed journals Surgery articles Surgery Research articles Surgery review articles Surgery PubMed articles Surgery PubMed Central articles Surgery 2023 articles Surgery 2024 articles Surgery Scopus articles Surgery impact factor journals Surgery Scopus journals Surgery PubMed journals Surgery medical journals Surgery free journals Surgery best journals Surgery top journals Surgery free medical journals Surgery famous journals Surgery Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
1. Case Report
A 76 year old female previously diagnosed with gout and hypertension was referred to orthopedic evaluation from her physiotherapist, after incidental discovery of a large infrascapular tumor on the right side. There were no mechanical symptoms, or symptoms suspect for malignancy. The patient was a former hairdresser, with a history of several years of manual labor, and was right handed. There was no family history of thoracic wall tumors. The primary physician referred the patient to ultrasound examination, which showed a subfacial tumor, with no other defining characteristics. The primary suspicion was an atypical lipoma.
At the primary physical examination a fixated, subscapular tumor measuring 5 by 5 centimeters was found. There was no soreness or pain, and shoulder mobility was unaffected. There were no breast tumors, cervical or axillary lymphadenopathy. The upper extremity was intact neurovascularly. No tumor was found under the left scapula.
MRI of the right scapular region showed a contrast enhancing, uniform and streaky mass interpositioned between the subscapularis muscle and the posterior thoracic wall, without involvement of the costae. The left side was imaged for comparison, and showed an equally located but marginally smaller mass. Upon secondary physical examination this tumor could also be found by the physician. The MRI showed no signs of malignancy (Figure 1 and 2).
These findings were discussed in a multidisciplinary tumor conference, with the conclusion that the masses represented bilateral ED. The patient was presented with treatment options in the form of conservative/no treatment or operation with non radical resection under general anaesthesia. Due to the scarcity of symptoms, weighed against inherent risks in surgery, the patient refrained from resection, with the possibility of seeking orthopedic consultation in the future in case of occurrence of symptoms and a desire for operative treatment.
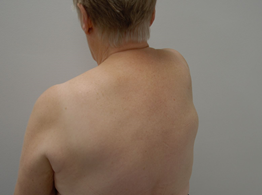
Figure 1: The patient presenting the mass located beneath the right scapula.
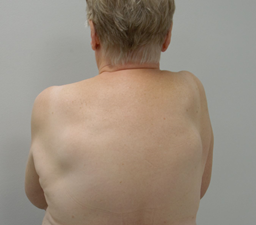
Figure 2: The patient presenting the bilateral masses at follow up visit.
2. Discussion
ED is an infrequently diagnosed benign condition, consisting of a slowly growing and often asymptomatic tumor located infra- or subscapularly. The literature describes a relatively common appearance of ED, although it is likely under diagnosed due to its often asymptomatic nature [3]. On the other hand, more rapidly growing and symptomatic cases of ED have also been reported. The diagnosis is made from MRI, or alternatively by biopsy or pathology examination after resection of the mass. The condition does not require treatment, unless the patient presents with pain or decreased functioning of the upper extremety. The treatment consists of surgical resection, and recurrence has not been described in the literature, even after non-radical resection. The surgery is safe, efficient, and leads to good functional outcome [1, 2]. The risks of surgery consist of damaging nerves and vessels, postoperative infection, and postoperative seroma or hematoma, which might require draining. No lasting sequelae have been described.
In regard to differential diagnostics, one should consider the benign and malignant chest wall tumors. The benign tumors consist largely of fibrous dysplasia, hemangioma, lipoma and schwannoma. Malignancy should be considered, especially in large and rapidly growing tumors. The most common primary malignant tumor of the chest wall is sarcoma, whereof 55% are chondro- and osteosarcomas, and 45% are soft tissue sarcomas. Approximately 60% of all primary chest wall tumors are malignant, but these tumors account for just 1-2% of all thoracic cancers [4, 5]. In addition to these tumors, other forms of cancer are known to metastasize to the chest wall. As such, it is important to examine chest wall tumors with CT and/or MRI, and to consider PET-scan and biopsy.
This case presents dorsal elastofibroma as a relevant differential diagnosis in chest wall tumors, and provides an example of diagnostic procedures and treatment of the condition. Diagnosing the condition can be done non-invasively, and surgery is rarely necessary.
Conflicts of Interest
None. The article submitted is neither published nor is under consideration by any other journal.
References
- Briccoli A, Casadei R, Di Renzo M, et al. Elastofibroma Dorsi. Surgery Today 30 (2000): 147-152.
- Daigeler A, Vogt PM, Busch K, et al. Elastofibroma Dorsi - differential diagnosis in chest wall tumors. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 5 (2007): 15.
- Jarvi OH, Lamsimies PH. Subclinical elastofibroma in an autopsy series: additional notes on the aetiology and pathogenesis of elastofibroma pseudoneoplasm. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 83 (1975): 87-108.
- Schick S, Zembsch A, Gahleitner A, et al. Atypical Appearance of Elastofibroma Dorsi on MRI: Case Reports and Review of the Literature. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography 2 (2000): 288-292.
- Cipriano A, Burfeind W. Management of Primary Soft Tissue Tumors of the Chest Wall. Thoracic Surgery Clinics. doi:10.1016/j.thorsurg. 2017.01.007.
