A Rare Case of Acute Postrenal Failure after Prostate Surgery
Article Information
Amandine Degraeve1*, Gilles Tilmans2, Francis Lorge1, Christophe Dossin3, Guillaume Krings1, Marcello Di Gregorio1, Gilles Adans Dester1, Julien Van Damme1
1Department of Urology, Université Catholique de Louvain, Namur, Belgium
2Department of Abdominal Surgery, Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc, Université Catholique de Louvain, Brussels, Belgium
3Department of Radiology, Université Catholique de Louvain, Namur, Belgium
*Corresponding Author: Amandine Degraeve, Department of Urology, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Université Catholique de Louvain, Rue Docteur Gaston Therasse, 5530 Yvoir, Namur, Belgium
Received: 30 May 2021; Accepted: 21 June 2021; Published: 01 July 2021
Citation: Amandine Degraeve, Gilles Tilmans, Francis Lorge, Christophe Dossin, Guillaume Krings, Marcello Di Gregorio, Gilles Adans Dester, Julien Van Damme. A Rare Case of Acute Postrenal Failure after Prostate Surgery. Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports 5 (2021): 520-525.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
In patients with acute ureteral obstruction, rapid increase in ureteral pressure results in dilatation of the ureter and intrarenal collecting system that usually may cause renal colic. Computed tomography and ultrasound are the gold standard to evaluate uretero-hydronephrosis. We report a case of a patient who underwent a robot-assisted radical prostatectomy for cancer and developed anuria in the immediate postoperative course without pain or hydronephrosis. Clinical and conventional imaging can be normal in case of acute post-renal failure.
Keywords
Acute renal failure; Prostate surgery; Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy
Acute renal failure articles; Prostate surgery articles; Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy articles
Acute renal failure articles Acute renal failure Research articles Acute renal failure review articles Acute renal failure PubMed articles Acute renal failure PubMed Central articles Acute renal failure 2023 articles Acute renal failure 2024 articles Acute renal failure Scopus articles Acute renal failure impact factor journals Acute renal failure Scopus journals Acute renal failure PubMed journals Acute renal failure medical journals Acute renal failure free journals Acute renal failure best journals Acute renal failure top journals Acute renal failure free medical journals Acute renal failure famous journals Acute renal failure Google Scholar indexed journals Prostate surgery articles Prostate surgery Research articles Prostate surgery review articles Prostate surgery PubMed articles Prostate surgery PubMed Central articles Prostate surgery 2023 articles Prostate surgery 2024 articles Prostate surgery Scopus articles Prostate surgery impact factor journals Prostate surgery Scopus journals Prostate surgery PubMed journals Prostate surgery medical journals Prostate surgery free journals Prostate surgery best journals Prostate surgery top journals Prostate surgery free medical journals Prostate surgery famous journals Prostate surgery Google Scholar indexed journals surgery articles surgery Research articles surgery review articles surgery PubMed articles surgery PubMed Central articles surgery 2023 articles surgery 2024 articles surgery Scopus articles surgery impact factor journals surgery Scopus journals surgery PubMed journals surgery medical journals surgery free journals surgery best journals surgery top journals surgery free medical journals surgery famous journals surgery Google Scholar indexed journals COVD-19 articles COVD-19 Research articles COVD-19 review articles COVD-19 PubMed articles COVD-19 PubMed Central articles COVD-19 2023 articles COVD-19 2024 articles COVD-19 Scopus articles COVD-19 impact factor journals COVD-19 Scopus journals COVD-19 PubMed journals COVD-19 medical journals COVD-19 free journals COVD-19 best journals COVD-19 top journals COVD-19 free medical journals COVD-19 famous journals COVD-19 Google Scholar indexed journals Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy articles Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy Research articles Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy review articles Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy PubMed articles Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy PubMed Central articles Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy 2023 articles Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy 2024 articles Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy Scopus articles Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy impact factor journals Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy Scopus journals Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy PubMed journals Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy medical journals Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy free journals Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy best journals Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy top journals Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy free medical journals Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy famous journals Non-dilatated obstructive uropathy Google Scholar indexed journals treatment articles treatment Research articles treatment review articles treatment PubMed articles treatment PubMed Central articles treatment 2023 articles treatment 2024 articles treatment Scopus articles treatment impact factor journals treatment Scopus journals treatment PubMed journals treatment medical journals treatment free journals treatment best journals treatment top journals treatment free medical journals treatment famous journals treatment Google Scholar indexed journals CT articles CT Research articles CT review articles CT PubMed articles CT PubMed Central articles CT 2023 articles CT 2024 articles CT Scopus articles CT impact factor journals CT Scopus journals CT PubMed journals CT medical journals CT free journals CT best journals CT top journals CT free medical journals CT famous journals CT Google Scholar indexed journals radiology articles radiology Research articles radiology review articles radiology PubMed articles radiology PubMed Central articles radiology 2023 articles radiology 2024 articles radiology Scopus articles radiology impact factor journals radiology Scopus journals radiology PubMed journals radiology medical journals radiology free journals radiology best journals radiology top journals radiology free medical journals radiology famous journals radiology Google Scholar indexed journals Abdominal surgery articles Abdominal surgery Research articles Abdominal surgery review articles Abdominal surgery PubMed articles Abdominal surgery PubMed Central articles Abdominal surgery 2023 articles Abdominal surgery 2024 articles Abdominal surgery Scopus articles Abdominal surgery impact factor journals Abdominal surgery Scopus journals Abdominal surgery PubMed journals Abdominal surgery medical journals Abdominal surgery free journals Abdominal surgery best journals Abdominal surgery top journals Abdominal surgery free medical journals Abdominal surgery famous journals Abdominal surgery Google Scholar indexed journals uropathy articles uropathy Research articles uropathy review articles uropathy PubMed articles uropathy PubMed Central articles uropathy 2023 articles uropathy 2024 articles uropathy Scopus articles uropathy impact factor journals uropathy Scopus journals uropathy PubMed journals uropathy medical journals uropathy free journals uropathy best journals uropathy top journals uropathy free medical journals uropathy famous journals uropathy Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
1. Introduction
Acute renal failure (ARF) appears in 0.8% in post-operative course after noncardiac surgery in patients with previously normal renal function (RF) [1]. Ultrasonography (US) or computed tomography (CT) are the imaging modalities of choice in the evaluation of ARF. Dilatation of the ureter and renal collecting system shown on imagery evaluation, should guide toward a post renal obstruction cause. Normal finding on imagery evaluation should lead to renal or prerenal causes [2]. In rare case, absence of dilatation of the urinary tract does not exclude the presence of obstruction [2]. We will discuss the etiology of non-dilatated obstructive uropathy (NDOU) and will propose a diagnostic and a management strategy.
2. Case Report
A 69-year-old man underwent a radical prostatectomy (RP) and bilateral lymph node dissection by robot-assisted laparoscopy for localized prostatic adenocarcinoma. The preoperative RF was normal. Past medical history included arterial hypertension and hepatitis A. He presented an ASA status of II and a body mass index of 23 kg/m². The day after his surgery he developed an ARF grade 4 with glomerular filtration rate (GFR) at 23ml/’/1.73m2, oligo-anuria (100 – 500 mL/24h) and an anuria the days after (<100 mL/24h). A urinary tract US (UTUS) was performed and didn’t show any abnormality (Figure 1). The urinary and blood ionograms were not in favor of a functional origin. The urine sediment analysis, the negative urine culture, the 24 hours proteinuria and electrophoresis for protein assessment did not highlight an organic origin. Subsequent US and CT performed on the 2th and 3th post-operative days revealed no peri-renal infiltration or urinary tract dilatation (Figure 2). Clinically, the patient was hemodynamically stable without any vasopressor therapy and did not describe any para-lumbar pain. The lumbar shaking was negative bilaterally. Biologically, his RF deteriorated rapidly (Table 1). Two dialysis sessions were necessary on post-operative day 4th and 5th.
We performed percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN) on the right side on post-operative day 5th and on the following day on the left side. Prograde opacification detected an obstruction at the uretero-vesical junction without ureterohydronephrosis. Immediate diuresis followed those procedures. GFR was back on baseline on post-drainage day 3th and kept stable afterwards (Table 1). One week after PCN, we performed an endoscopic exploration. Two JJ stents were placed easily. The two ureteral meatus were away from the vesico-urethral suture. There was a significant inflammatory reaction with the presence of edematous tissues on the urinary bladder trigone, cause of the bilateral obstruction. JJ stents were removed after 6 weeks with a stable RF and no dilatation of the renal collecting system on UTUS.
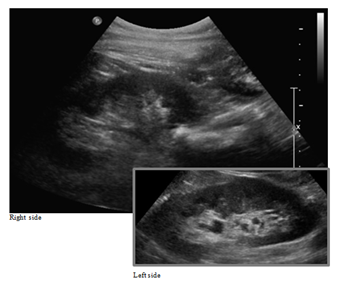
Figure 1: US performed on the first day after surgery.
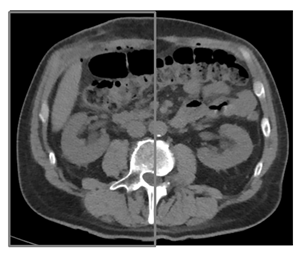
Figure 2: Reconstructed CT performed on the second day after surgery.
|
Urea (19-43 mg/dL) |
Créatinine (0.66-1.25 mg/dL) |
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR mL/min/1.73 m²) |
Acute renal failure GRADE |
|
|
Month -3 |
38 |
0.86 |
93.54 |
1 |
|
Day +1 |
70 |
2.82 |
23.45 |
4 |
|
Day +2 |
90 |
5.81 |
10.31 |
5 |
|
Day +3 |
104 |
7.37 |
7.84 |
5 |
|
Day +4 |
117 |
9.19 |
6.07 |
5 |
|
Day +5 |
104 |
9.80 |
5.64 |
5 |
|
Urine drainage +1 |
61 |
4.51 |
13.81 |
5 |
|
Urine drainage +2 |
30 |
1.06 |
53.43 |
3 |
|
Urine drainage +3 |
21 |
0.68 |
122.57 |
1 |
|
Day +19 |
37 |
0.86 |
93.46 |
1 |
|
Day +2 JJ stents removal |
30 |
0.79 |
103 |
1 |
Table 1: Biologic follow up after surgery.
3. Discussion
It is estimated that ureteric injuries happen in less than 0.05% of cases during robotic RP [3, 4]. ARF occurs less than <0.5% after RP surgery and in 0.9% with the need of interventional procedure (endoscopic, percutaneous or surgery) due to presence of obstructive mechanism. Around 4% and 5% of patients with an obstructive uropathy present a NDOU [2].We present a case of a patient with ARF and anuria after RP with NDOU. The combination of these two conditions is therefore exceptional.
To our knowledge, few results like this have been reported and none in a direct post-operative context of robotic RP without ligature of the ureters [2, 5, 6]. The more frequent aetiologia of bilateral ureteral obstruction is malignancy (80%) [5]. The benign causes (20%) are stones, retroperitoneal fibrosis, acute bleeding, papillary necrosis, infection, iatrogenic injuries, ureteral vasculitis, pregnancy and finally varia as complete scrotal urinary bladder herniation, detrusor hypertrophy or bladder wall oedema after surgery [5]. The latter case is usually described after hysterectomy but not after RP.
Hydronephrosis is usually the result of physiologic changes, linked to both duration and severity of obstruction [7]. There are imaging false negative tests, the so-called syndrome of NDOU. The exact cause of the absence of dilatation is not clear. Clinical conditions associated with the absence of hydronephrosis on US and CT-scan despite obstructed kidneys include acute early obstruction, the presence of retroperitoneal fibrosis, dehydration or septic shock [5]. Our patient was well infused and had normal vital parameters. The physiopathology could be an absence of increased pressure inside the cavities or a modification in the physical properties of the urinary tract wall – the parietal layer [2]. It could also be due to a particular morphology of the renal pelvis. The latter can be considered in our case. The renal pelvis was small, formed by the confluence of the calyces. This particular anatomic pattern was found in similar cases [2, 6]. Other factors as location, nature, acuteness of the obstruction could be considered as the cause of the absence of dilatation.
CT and US are both imaging modalities of choice to determine the location and the cause of a urinary obstruction [8]. MAG3-lasix scintigraphy is a noninvasive, widely available test that can evaluate renal function and urine transit in a single procedure [9]. This test is useful to affirm a urinary tract obstruction but do not locate this one. Antegrade pyelography is a good way to achieve opacification of the urinary tract. In our study case, the problem was the pain felt by the patient when injecting the contrast. This approach allows the placement of nephrostomy or antegrade JJ stent with success rates of up to 95% [10]. Endoscopic exploration with retrograde pyelography allows both determine the location of the obstacle and set up ureteral retrograde catheter. In our case, the operation was easy but can be complicated in oncological cases with success rate of around 50% [10]. Given the intraoperative diagnosis of local edema, administration of corticosteroids could have been beneficial.
4. Conclusion
Acute renal failure after radical prostatectomy with a non-dilatated obstructive uropathy is rare. When ARF develops in a setting with a high probability of ureteral obstruction, this diagnosis should be vigorously pursued despite absence of clinical symptoms or normal radiologic results. A small pelvis formed by the confluence of the calyces could be an anatomical characteristic related to the absence of hydronephrosis. Left undiagnosed, this potentially reversible cause of renal failure can lead to end-stage renal disease.
Declaration of Interest
All authors disclose any financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence (bias) this work.
Statement of Ethics
The patient has given their written informed consent to publish their case.
References
- Kheterpal S, Tremper KK, Englesbe MJ, et al. Predictors of postoperative acute renal failure after noncardiac surgery in patients with previously normal renal function. Anesthesiology 107 (2007): 892-902.
- Maillet PJ, Pelle-Francoz D, Laville M, et al. Nondilated obstructive acute renal failure: diagnostic procedures and therapeutic management. Radiology 160 (1986): 659-662.
- Petrella F, Anidjar M. Postoperative Management of Ectopic Ureter Injury After Robotic-assisted Radical Prostatectomy: A Case Report. Urology 143 (2020): e20-e23.
- Jhaveri JK, Penna FJ, Diaz-Insua M, et al. Ureteral injuries sustained during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. J Endourol 28 (2014): 318-324.
- Schattner A, Drahy Y, Dubin I. The bladder ran dry: bilateral ureteral obstruction. BMJ Case Rep (2017).
- Rascoff JH, Golden RA, Spinowitz BS, et al. Nondilated obstructive nephropathy. Arch Intern Med 143 (1983): 696-698.
- Smith RC, Verga M, Dalrymple N, et al. Acute ureteral obstruction: value of secondary signs of helical unenhanced CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 167 (1996): 1109-1113.
- Sheafor DH, Hertzberg BS, Freed KS, et al. Nonenhanced helical CT and US in the emergency evaluation of patients with renal colic: prospective comparison. Radiology 217 (2000): 792-797.
- Taylor AT, Brandon DC, de Palma D, et al. SNMMI Procedure Standard/EANM Practice Guideline for Diuretic Renal Scintigraphy in Adults With Suspected Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction 1.0. Semin Nucl Med 48 (2018): 377-390.
- Turgut B, Bayraktar AM, Bakdik S, et al. Placement of double-J stent in patients with malignant ureteral obstruction: antegrade or retrograde approach?. Clin Radiol 74 (2019): 976.e11-976.e17.
